Magnetoacoustic imaging of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles embedded in biological tissues with microsecond magnetic stimulation
- PMID: 22271933
- PMCID: PMC3262848
- DOI: 10.1063/1.3675457
Magnetoacoustic imaging of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles embedded in biological tissues with microsecond magnetic stimulation
Abstract
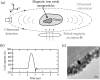
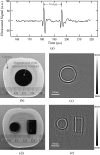
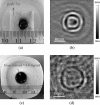
We present an experimental study on magnetoacoustic imaging of superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles embedded in biological tissues. In experiments, a large-current-carrying coil is used to deliver microsecond pulsed magnetic stimulation to samples. The ultrasound signals induced by magnetic forces on SPIO nanoparticles are measured by a rotating transducer. The distribution of nanoparticles is reconstructed by a back-projection imaging algorithm. The results demonstrated the feasibility to obtain cross-sectional image of magnetic nanoparticle targets with faithful dimensional and positional information, which suggests a promising tool for tomographic reconstruction of magnetic nanoparticle-labeled diseased tissues (e.g., cancerous tumor) in molecular or clinic imaging.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thermoacoustic Imaging and Therapy Guidance based on Ultra-short Pulsed Microwave Pumped Thermoelastic Effect Induced with Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles.Theranostics. 2017 May 11;7(7):1976-1989. doi: 10.7150/thno.17846. eCollection 2017. Theranostics. 2017. PMID: 28638483 Free PMC article.
-
The Imaging of Magnetic Nanoparticles with Low-power Magnetoacoustic Tomography.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2021 Nov;2021:2696-2699. doi: 10.1109/EMBC46164.2021.9630172. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2021. PMID: 34891807
-
Novel reconstruction algorithm of magnetoacoustic tomography based on ring transducer array for acoustic speed inhomogeneous tissues.Med Phys. 2020 Aug;47(8):3533-3544. doi: 10.1002/mp.14210. Epub 2020 May 23. Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 32343838
-
Current state and future applications of active targeting in malignancies using superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles.Cancer Biomark. 2009;5(2):99-107. doi: 10.3233/CBM-2009-0615. Cancer Biomark. 2009. PMID: 19414927 Review.
-
A comprehensive literatures update of clinical researches of superparamagnetic resonance iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2017 Feb;7(1):88-122. doi: 10.21037/qims.2017.02.09. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2017. PMID: 28275562 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Vivo Electrical Conductivity Contrast Imaging in a Mouse Model of Cancer Using High-Frequency Magnetoacoustic Tomography With Magnetic Induction (hfMAT-MI).IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016 Oct;35(10):2301-2311. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2016.2560146. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27834641 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic mediators for ultrasound theranostics.Theranostics. 2021 Nov 2;11(20):10091-10113. doi: 10.7150/thno.62218. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34815806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetic particle mapping using magnetoelectric sensors as an imaging modality.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 14;9(1):2086. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38451-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30765847 Free PMC article.
-
Magneto acoustic tomography with short pulsed magnetic field for in-vivo imaging of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles.Nanomedicine. 2016 Apr;12(3):689-699. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2015.10.014. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 26656627 Free PMC article.
-
A preliminary in vivo study of a method for measuring magneto-acoustic sonic source under electrical stimulation.Technol Health Care. 2020;28(S1):421-432. doi: 10.3233/THC-209043. Technol Health Care. 2020. PMID: 32364175 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
