Neurogenesis in Neurotoxin-induced Animal Models for Parkinson's Disease-A Review of the Current Status
- PMID: 22271983
- PMCID: PMC3246055
- DOI: 10.1293/tox.22.101
Neurogenesis in Neurotoxin-induced Animal Models for Parkinson's Disease-A Review of the Current Status
Abstract
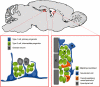
Animal models for Parkinson's disease (PD) are essential for understanding its pathogenesis and for development and testing of new therapies. Discoveries of endogenous neurogenesis in the adult mammalian brain give new insight into the cell-based approach for treatment of neurodegenerative disorders, such as PD. Although a great deal of interest has been focused on endogenous neurogenesis in neurotoxin-induced animal models for PD, it still remains controversial whether neural stem cells migrate into the injured area and contribute to repopulation of depleted dopaminergic neurons in neurotoxin-injured adult brains. The purpose of this review is to examine the data available regarding neurogenesis in neurotoxin-induced animal models of PD. It is hoped that data from the animal investigations available in the literature will promote understanding of the neurotoxin-induced animal models for PD.
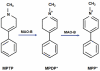
Keywords: 6-OHDA; MPTP; Parkinson’s disease; animal model; neurogenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal stem cells augment neurogenesis in the subventricular zone and enhance differentiation of neural precursor cells into dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra of a parkinsonian model.Cell Transplant. 2012;21(8):1629-40. doi: 10.3727/096368912X640556. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Cell Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22546197
-
Brain-specific NRSF deficiency aggravates dopaminergic neurodegeneration and impairs neurogenesis in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 May 30;11(10):3280-3297. doi: 10.18632/aging.101979. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31147527 Free PMC article.
-
Endurance Exercise Mediates Neuroprotection Against MPTP-mediated Parkinson's Disease via Enhanced Neurogenesis, Antioxidant Capacity, and Autophagy.Neuroscience. 2018 May 21;379:292-301. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.03.015. Epub 2018 Mar 17. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 29559387
-
Harnessing neurogenesis for the possible treatment of Parkinson's disease.J Comp Neurol. 2014 Aug 15;522(12):2817-30. doi: 10.1002/cne.23607. Epub 2014 May 9. J Comp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24723264 Review.
-
Resident adult neural stem cells in Parkinson's disease--the brain's own repair system?Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Nov 5;719(1-3):117-127. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.04.058. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23872414 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurotoxicity and Underlying Mechanisms of Endogenous Neurotoxins.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 26;22(23):12805. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312805. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes of MAO-A and MAO-B Expressions in the Placenta of MPTP or MPP(+) Treated Mice.J Toxicol Pathol. 2013 Mar;26(1):73-7. doi: 10.1293/tox.26.73. Epub 2013 Apr 22. J Toxicol Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23723572 Free PMC article.
-
Neurogenic effects of rotarod walking exercise in subventricular zone, subgranular zone, and substantia nigra in MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease mice.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 22;12(1):10544. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14823-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35732806 Free PMC article.
-
Korean Red Ginseng Enhances Neurogenesis in the Subventricular Zone of 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine-Treated Mice.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Nov 6;10:355. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00355. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30459594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkinson J. An essay on the shaking palsy. 1817. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 14: 223–236, discussion 222 2002 - PubMed
-
- Borta A, Hoglinger GU. Dopamine and adult neurogenesis. J Neurochem. 100: 587–595 2007 - PubMed
-
- Przedborski S, Ischiropoulos H. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: weapons of neuronal destruction in models of Parkinson’s disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 7: 685–693 2005 - PubMed
-
- Simola N, Morelli M, Carta AR. The 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox Res. 11: 151–167 2007 - PubMed
-
- Perese DA, Ulman J, Viola J, Ewing SE, Bankiewicz KS. A 6-hydroxydopamine-induced selective parkinsonian rat model. Brain Res. 494: 285–293 1989 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
