Thy-1 Expressing Mesenchymal Cells in Rat Nephrogenesis in Correlation with Cells Immunoreactive for α-Smooth Muscle Actin and Vimentin
- PMID: 22272005
- PMCID: PMC3234650
- DOI: 10.1293/tox.23.1
Thy-1 Expressing Mesenchymal Cells in Rat Nephrogenesis in Correlation with Cells Immunoreactive for α-Smooth Muscle Actin and Vimentin
Abstract
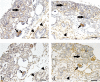
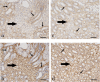
Thy-1 expression may influence myofibroblast development. Through the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), injured renal epithelial cells undergo regression to the metanephric mesenchymal phenotype and then acquire a myofibroblastic nature (expressing α-smooth muscle actin; α-SMA). Because the metanephric blastema differentiates into mesenchymal and renal epithelial cells, we investigated Thy-1 immunoexpression during nephrogenesis in F344 rats in correlation with vimentin and α-SMA expressions. Kidney samples were obtained from fetuses on gestation days 18 and 21, neonates on days 1-18 and adults at 6 weeks of age. Mesangial cells in S-shaped bodies and immature and mature glomeruli continuously expressed both Thy-1 and α-SMA during early nephrogenesis (fetuses and neonates on days 1-9). During early nephrogenesis, loosely-arranged blastemal cell-derived mesenchymal cells in the cortex and medulla also exhibited Thy-1 and α-SMA, although the α-SMA expression was weaker than that of Thy-1. Vimentin expression coincided with that of Thy-1. These findings indicate that the derivation of α-SMA-expressing myofibroblastic cells may be related to mesangial or blastemal cells expressing both Thy-1 and α-SMA. Interestingly, there was a difference in Thy-1 expression between cortical and medullary tubulointerstitial cells from late nephrogenesis (neonates on days 12-18) and those from adults in that the cortical cells reacted faintly or negatively to Thy-1, whereas the medullary cells reacted strongly to Thy-1; additionally, bundle-arranged mesenchymal cells that were only observed in the neonates on days 1-12 reacted strongly to α-SMA, but faintly to Thy-1. Blastemal cell-derived mesenchymal cells seem to alter the immunoexpressions of Thy-1 and α-SMA, depending on the conditions which they develop. Thy-1 immunoexpression would be useful for investigation of reverse embryogenesis, which might occur in fibrotic kidneys.
Keywords: Thy-1; blastemal cells; myofibroblasts; nephrogenesis; rat; α-smooth muscle actin.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Thy-1 expression, a possible marker of early myofibroblast development, in renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis induced in rats by cisplatin.Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2013 Jul;65(5):651-9. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2012.07.005. Epub 2012 Aug 11. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2013. PMID: 22884260
-
Differential immunoexpressions of cytoskeletons in renal epithelial and interstitial cells in rat and canine fibrotic kidneys, and in kidney-related cell lines under fibrogenic stimuli.Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2005 Nov;57(2):135-47. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2005.07.001. Epub 2005 Aug 15. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16325524
-
Immunophenotypical analyses of myofibroblasts in rat excisional wound healing: possible transdifferentiation of blood vessel pericytes and perifollicular dermal sheath cells into myofibroblasts.Histol Histopathol. 2012 Apr;27(4):515-27. doi: 10.14670/HH-27.515. Histol Histopathol. 2012. PMID: 22374729
-
Myofibroblast phenotypes expression in experimental renal scarring.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997 May;12(5):904-15. doi: 10.1093/ndt/12.5.904. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997. PMID: 9175042
-
Immunophenotypical analysis of myofibroblasts and mesenchymal cells in the bleomycin-induced rat scleroderma, with particular reference to their origin.Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2013 Jul;65(5):567-77. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2012.05.002. Epub 2012 Jun 30. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2013. PMID: 22749686
Cited by
-
Stem cell pathology: histogenesis of malignant fibrous histiocytoma and characterization of myofibroblasts appearing in fibrotic lesions.J Vet Med Sci. 2023 Sep 1;85(9):895-906. doi: 10.1292/jvms.23-0225. Epub 2023 Jul 17. J Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37460298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calponin expression in renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis induced in rats by Cisplatin.J Toxicol Pathol. 2014 Apr;27(1):97-103. doi: 10.1293/tox.2013-0048. Epub 2014 Apr 30. J Toxicol Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24791074 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of CD90/Thy-1 as a crucial molecular signature for myogenic differentiation in human urine-derived cells through single-cell RNA sequencing.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 28;14(1):2329. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52530-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38282008 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Thy-1 Antibody-mediated Complement-dependent Cytotoxicity is Regulated by the Distribution of Antigen, Antibody and Membrane Complement Regulatory Proteins in Rats.J Toxicol Pathol. 2013 Mar;26(1):41-9. doi: 10.1293/tox.26.41. Epub 2013 Apr 22. J Toxicol Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23723567 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of Type 2 Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Renal and Hepatic Fibrosis.J Clin Med. 2015 Dec 30;5(1):4. doi: 10.3390/jcm5010004. J Clin Med. 2015. PMID: 26729181 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nigam SK, Aperia AC, Brenner BM.Development and maturation of the kidney. In: The Kidney, 5th ed. Brenner BM (ed). W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia. 72–98.1996.
-
- Eddy AA. Molecular insights into renal interstitial fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996;7:2495–2508. - PubMed
-
- Yamate J, Kuribayashi M, Kuwamura M, Kotani T, Ogihara K. Differential immunoexpressions of cytoskeletons in renal epithelial and interstitial cells in rat and canine fibrotic kidneys, and in kidney-related cell lines under fibrogenic stimuli. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2005;57:135–147. - PubMed
-
- Sappino AP, Schürch W, Gabbiani G. Differentiation repertoire of fibroblastic cells: expression of cytoskeletal proteins as marker of phenotypic modulations. Lab Invest. 1990;63:144–161. - PubMed
-
- Fan JM, Ng YY, Hill PA, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Mu W, Atkins RC, Lan HY. Transforming growth factor-beta regulates tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation in vitro. Kidney Int. 1999;56:1455–1467. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
