Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) associated with histopathological changes in rodent models of osteoarthritis
- PMID: 22272053
- PMCID: PMC3234605
- DOI: 10.1293/tox.24.137
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) associated with histopathological changes in rodent models of osteoarthritis
Abstract
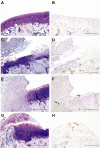
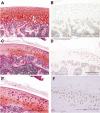
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors have recently reported to be expressed in human osteoarthritis (OA), suggesting that VEGF could be implicated in the pathogenesis of this disease. In the present study, expression of VEGF in the articular cartilage was determined in three different OA models: medial meniscectomy and monoiodoacetate (MIA) injection in rats and age-associated spontaneous joint cartilage destruction in guinea pigs. VEGF was detected by immunohistochemical analysis in the regenerative and hypertrophic chondrocytes, perichondrium and osteophyte areas and chondrocyte clones. Stain intensity of VEGF immunoreactivity increased simultaneously with the degree of cartilage destruction and reparation. These results suggest that VEGF is a key factor in the articular cartilage in human OA and animal OA models.
Keywords: Immunohistochemistry; Medial meniscectomy; Monoiodoacetate (MIA); Osteoarthritis; Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms and their receptors are expressed in human osteoarthritic cartilage.Am J Pathol. 2003 Jan;162(1):171-81. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63808-4. Am J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12507900 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is expressed during articular cartilage growth and re-expressed in osteoarthritis.Ann Acad Med Singap. 2010 May;39(5):399-403. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2010. PMID: 20535432
-
Development and regulation of osteophyte formation during experimental osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2002 Mar;10(3):180-7. doi: 10.1053/joca.2001.0505. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2002. PMID: 11869078
-
The influence of biomechanical parameters on the expression of VEGF and endostatin in the bone and joint system.Ann Anat. 2005 Nov;187(5-6):461-72. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2005.06.008. Ann Anat. 2005. PMID: 16320826 Review.
-
The potential role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in cartilage: how the angiogenic factor could be involved in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis?Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008 Mar;16(3):279-86. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2007.09.003. Epub 2007 Oct 22. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008. PMID: 17945514 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatocyte growth factor increases vascular endothelial growth factor-A production in human synovial fibroblasts through c-Met receptor pathway.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50924. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050924. Epub 2012 Nov 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23209838 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of low-level laser therapy on the expression of inflammatory mediators and on neutrophils and macrophages in acute joint inflammation.Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(5):R116. doi: 10.1186/ar4296. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 24028507 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of synoviocyte activity by resveratrol in rats with adjuvant arthritis.Exp Ther Med. 2013 Jul;6(1):172-176. doi: 10.3892/etm.2013.1078. Epub 2013 Apr 25. Exp Ther Med. 2013. PMID: 23935741 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine profiles in the joint depend on pathology, but are different between synovial fluid, cartilage tissue and cultured chondrocytes.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Sep 26;16(5):441. doi: 10.1186/s13075-014-0441-0. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25256035 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of sensory innervation in synovium of rats within different knee osteoarthritis models and the correlation between synovial fibrosis and hyperalgesia.J Adv Res. 2021 Jun 15;35:141-151. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.06.007. eCollection 2022 Jan. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 35003798 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hayami T, Pickarski M, Wesolowski GA, McLane J, Bone A, Destefano J, Rodan GA, Duong le T.The role of subchondral bone remodeling in osteoarthritis: reduction of cartilage degeneration and prevention of osteophyte formation by alendronate in the rat anterior cruciate ligament transection model. Arthritis Rheum. 50: 1193–1206 2004 - PubMed
-
- Janusz MJ, Hookfin EB, Heitmeyer SA, Woessner JF, Freemont AJ, Hoyland JA, Brown KK, Hsieh LC, Almstead NG, De B, Natchus MG, Pikul S, Taiwo YO. Moderation of iodoacetate-induced experimental osteoarthritis in rats by matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 9: 751–760 2001 - PubMed
-
- Janusz MJ, Bendele AM, Brown KK, Taiwo YO, Hsieh L, Heitmeyer SA. Induction of osteoarthritis in the rat by surgical tear of the meniscus: Inhibition of joint damage by a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 10: 785–791 2002 - PubMed
-
- Baragi VM, Becher G, Bendele AM, Biesinger R, Bluhm H, Boer J, Deng H, Dodd R, Essers M, Feuerstein T, Gallagher BM, Jr, Gege C, Hochgürtel M, Hofmann M, Jaworski A, Jin L, Kiely A, Korniski B, Kroth H, Nix D, Nolte B, Piecha D, Powers TS, Richter F, Schneider M, Steeneck C, Sucholeiki I, Taveras A, Timmermann A, Van Veldhuizen J, Weik J, Wu X, Xia B. A new class of potent matrix metalloproteinase 13 inhibitors for potential treatment of osteoarthritis: Evidence of histologic and clinical efficacy without musculoskeletal toxicity in rat models. Arthritis Rheum. 60: 2008–2018 2009 - PubMed
-
- Botter SM, Glasson SS, Hopkins B, Clockaerts S, Weinans H, van Leeuwen JP, van Osch GJ. ADAMTS5-/- mice have less subchondral bone changes after induction of osteoarthritis through surgical instability: implications for a link between cartilage and subchondral bone changes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 17: 636–645 2009 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
