Knockdown of ephrin-A5 expression by 40% does not affect motor axon growth or migration into the chick hindlimb
- PMID: 22272077
- PMCID: PMC3257074
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms12128362
Knockdown of ephrin-A5 expression by 40% does not affect motor axon growth or migration into the chick hindlimb
Abstract
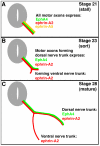
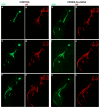
Bidirectional signaling between Eph receptor tyrosine kinases and their cell-surface protein signals, the ephrins, comprises one mechanism for guiding motor axons to their proper targets. During projection of motor axons from the lateral motor column (LMC) motor neurons of the spinal cord to the hindlimb muscles in chick embryos, ephrin-A5 has been shown to be expressed in the LMC motor axons until they reach the base of the limb bud and initiate sorting into their presumptive dorsal and ventral nerve trunks, at which point expression is extinguished. We tested the hypothesis that this dynamic pattern of ephrin-A5 expression in LMC motor axons is important for the growth and guidance of the axons to, and into, the hindlimb by knocking down endogenous ephrin-A5 expression in the motor neurons and their axons. No perturbation of LMC motor axon projections was observed in response to this treatment, suggesting that ephrin-A5 is not needed for LMC motor axon growth or guidance.
Keywords: chick; in ovo electroporation; motor neurons.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ephexin1 Is Required for Eph-Mediated Limb Trajectory of Spinal Motor Axons.J Neurosci. 2018 Feb 21;38(8):2043-2056. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2257-17.2018. Epub 2018 Jan 23. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29363583 Free PMC article.
-
Paxillin Is Required for Proper Spinal Motor Axon Growth into the Limb.J Neurosci. 2021 Apr 28;41(17):3808-3821. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2863-20.2021. Epub 2021 Mar 16. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33727334 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of EphA4, ephrin-A2 and ephrin-A5 during axon outgrowth to the hindlimb indicates potential roles in pathfinding.Dev Neurosci. 2000;22(3):237-50. doi: 10.1159/000017446. Dev Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10894987
-
Crossing the border: molecular control of motor axon exit.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(12):8539-61. doi: 10.3390/ijms12128539. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22272090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of neuromuscular connections: guidance of motoneuron axons to muscles in the embryonic chick hindlimb.Ciba Found Symp. 1988;138:97-115. doi: 10.1002/9780470513675.ch7. Ciba Found Symp. 1988. PMID: 3058436 Review.
Cited by
-
Transport and Secretion of the Wnt3 Ligand by Motor Neuron-like Cells and Developing Motor Neurons.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 17;11(12):1898. doi: 10.3390/biom11121898. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944540 Free PMC article.
-
The Ephrin-A5/EphA4 Interaction Modulates Neurogenesis and Angiogenesis by the p-Akt and p-ERK Pathways in a Mouse Model of TLE.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jan;53(1):561-576. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-9020-2. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25502292
References
-
- Egea J., Klein R. Bidirectional Eph-ephrin signaling during axon guidance. Trends Cell Biol. 2007;17:230–238. - PubMed
-
- Eberhart J., Swartz M.E., Koblar S.A., Pasquale E.B., Krull C.E. EphA4 constitutes a population-specific guidance cue for motor neurons. Dev. Biol. 2002;247:89–101. - PubMed
-
- Eberhart J., Swartz M., Koblar S.A., Pasquale E.B., Tanaka H., Krull C.E. Expression of EphA4, ephrin-A2, and ephrin-A5 during axon outgrowth to the hindlimb indicates potential roles in pathfinding. Dev. Neurosci. 2000;22:237–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

