Effects of soybean agglutinin on intestinal barrier permeability and tight junction protein expression in weaned piglets
- PMID: 22272087
- PMCID: PMC3257084
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms12128502
Effects of soybean agglutinin on intestinal barrier permeability and tight junction protein expression in weaned piglets
Abstract
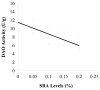
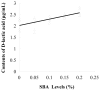
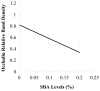
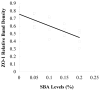
This study was developed to provide further information on the intestinal barrier permeability and the tight junction protein expression in weaned piglets fed with different levels of soybean agglutinin (SBA). Twenty-five weaned crossbred barrows (Duroc × Landrace × Yorkshire) were selected and randomly allotted to five groups, each group with five replicates. The piglets in the control group were not fed with leguminous products. 0.05, 0.1, 0.15 and 0.2% SBA was added to the control diet to form four experimental diets, respectively. After the experimental period of 7 days (for each group), all the piglets were anesthetized with excess procaine and slaughtered. The d-lactic acid in plasma and the Ileal mucosa diamine oxidase (DAO) was analyzed to observe the change in the intestinal permeability. The tight junction proteins occludin and ZO-1 in the jejunum tissue distribution and relative expression were detected by immunohistochemistry and Western Blot. The results illustrated that a high dose of SBA (0.1-0.2%) could increase the intestinal permeability and reduce piglet intestinal epithelial tight junction protein occludin or ZO-1 expression, while low dose of SBA (0.05% of total diet) had no significant affects. The contents of DAO, d-lactic acid, occludin or ZO-1, had a linear relationship with the SBA levels (0-0.2%) in diets. The high dose SBA (0.1-0.2%) could increase the intestinal permeability and reduce piglet intestinal epithelial tight junction protein occludin or ZO-1 expression, while low dose of SBA (0.05% of total diet) had no affects.
Keywords: ZO-1; intestinal permeability; occludin; piglets; soybean agglutinin; tight junction.
Figures

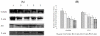
Similar articles
-
Effects of rhein on intestinal epithelial tight junction in IgA nephropathy.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jul 14;19(26):4137-45. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i26.4137. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23864776 Free PMC article.
-
Lactobacillus casei Zhang Prevents Jejunal Epithelial Damage to Early-Weaned Piglets Induced by Escherichia coli K88 via Regulation of Intestinal Mucosal Integrity, Tight Junction Proteins and Immune Factor Expression.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Jun 28;29(6):863-876. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1903.03054. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31091863
-
Effects of simulated weightlessness on tight junction protein occludin and Zonula Occluden-1 expression levels in the intestinal mucosa of rats.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011 Feb;31(1):26-32. doi: 10.1007/s11596-011-0145-5. Epub 2011 Feb 19. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21336719
-
A critical review on intestinal mucosal barrier protection effects of dietary polysaccharides.Food Funct. 2024 Jan 22;15(2):481-492. doi: 10.1039/d3fo03412g. Food Funct. 2024. PMID: 38197139 Review.
-
Looking Inside of the Intestinal Permeability Regulation by Protein-Derivatives from Bovine Milk.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2024 Nov;68(22):e2400384. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202400384. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2024. PMID: 39530631 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Feeding soy protein concentrates with low or high isoflavone decreases liver inflammation by reducing lipopolysaccharide translocation.Front Nutr. 2023 Nov 20;10:1278158. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1278158. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38075211 Free PMC article.
-
Maggot protein ameliorates dextran sulphate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice.Biosci Rep. 2018 Nov 28;38(6):BSR20181799. doi: 10.1042/BSR20181799. Print 2018 Dec 21. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30393231 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-high-pressure passivation of soybean agglutinin and safety evaluations.Food Chem X. 2023 May 27;18:100726. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.100726. eCollection 2023 Jun 30. Food Chem X. 2023. PMID: 37397201 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Intestinal Mucosa Integrity and GLP-2 Gene Functions upon Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection in Pigs.Animals (Basel). 2021 Mar 1;11(3):644. doi: 10.3390/ani11030644. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33804466 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal mucosal injury induced by obstructive jaundice is associated with activation of TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB pathways.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 31;14(10):e0223651. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223651. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31671112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gatel F. Protein quality of legume seeds for non-ruminant animals: A literature review. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 1994;45:317–348.
-
- King T.P., Begbie R., Cadenhead A. Nutritional toxicity of raw kidney beans in pigs. Immunocytochemical and cytopathological studies on the gutand the pancreas. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1983;34:1404–1412. - PubMed
-
- Sharon N., Lis H. Legume lectins—A large family of homologous proteins. FASEB J. 1990;4:3198–3208. - PubMed
-
- Valdebouze P., Bergeron E., Gaborit T., Delort-Laval J. Content and distribution of trypsin inhibitors and haemagglutinins in some legume seeds. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1980;60:695–701.
-
- Gupta Y.P. Anti-nutritional and toxic factors in food legumes: A review. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1987;37:201–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

