The Wnt and BMP families of signaling morphogens at the vertebrate neuromuscular junction
- PMID: 22272112
- PMCID: PMC3257109
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms12128924
The Wnt and BMP families of signaling morphogens at the vertebrate neuromuscular junction
Abstract
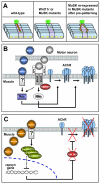
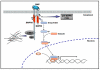
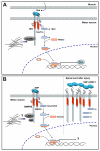
The neuromuscular junction has been extensively employed in order to identify crucial determinants of synaptogenesis. At the vertebrate neuromuscular synapse, extracellular matrix and signaling proteins play stimulatory and inhibitory roles on the assembly of functional synapses. Studies in invertebrate species have revealed crucial functions of early morphogens during the assembly and maturation of the neuromuscular junction. Here, we discuss growing evidence addressing the function of Wnt and Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathways at the vertebrate neuromuscular synapse. We focus on the emerging role of Wnt proteins as positive and negative regulators of postsynaptic differentiation. We also address the possible involvement of BMP pathways on motor neuron behavior for the assembly and/or regeneration of the neuromuscular junction.
Keywords: BMP; Wnt; neuromuscular junction.
Figures
References
-
- Sanes J.R., Lichtman J.W. Development of the vertebrate neuromuscular junction. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1999;22:389–442. - PubMed
-
- Sanes J.R., Lichtman J.W. Induction, assembly, maturation and maintenance of a postsynaptic apparatus. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001;2:791–805. - PubMed
-
- Fox M.A., Umemori H. Seeking long-term relationship: axon and target communicate to organize synaptic differentiation. J. Neurochem. 2006;97:1215–1231. - PubMed
-
- Kummer T.T., Misgeld T., Sanes J.R. Assembly of the postsynaptic membrane at the neuromuscular junction: paradigm lost. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2006;16:74–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

