Dynamic structure-based pharmacophore model development: a new and effective addition in the histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) inhibitor discovery
- PMID: 22272142
- PMCID: PMC3257139
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms12129440
Dynamic structure-based pharmacophore model development: a new and effective addition in the histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) inhibitor discovery
Abstract
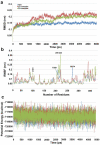
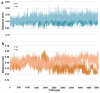
Histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) is an enzyme involved in deacetylating the amino groups of terminal lysine residues, thereby repressing the transcription of various genes including tumor suppressor gene. The over expression of HDAC8 was observed in many cancers and thus inhibition of this enzyme has emerged as an efficient cancer therapeutic strategy. In an effort to facilitate the future discovery of HDAC8 inhibitors, we developed two pharmacophore models containing six and five pharmacophoric features, respectively, using the representative structures from two molecular dynamic (MD) simulations performed in Gromacs 4.0.5 package. Various analyses of trajectories obtained from MD simulations have displayed the changes upon inhibitor binding. Thus utilization of the dynamically-responded protein structures in pharmacophore development has the added advantage of considering the conformational flexibility of protein. The MD trajectories were clustered based on single-linkage method and representative structures were taken to be used in the pharmacophore model development. Active site complimenting structure-based pharmacophore models were developed using Discovery Studio 2.5 program and validated using a dataset of known HDAC8 inhibitors. Virtual screening of chemical database coupled with drug-like filter has identified drug-like hit compounds that match the pharmacophore models. Molecular docking of these hits reduced the false positives and identified two potential compounds to be used in future HDAC8 inhibitor design.
Keywords: Lipinski’s rule; molecular docking; molecular dynamics simulation; pharmacophore; virtual screening.
Figures
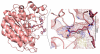
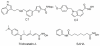
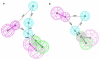
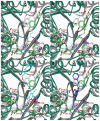
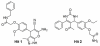
References
-
- Finnin M.S., Donigian J.R., Cohen A., Richon V.M., Rifkind R.A., Marks P.A., Breslow R., Pavletich N.P. Structures of a histone deacetylase homologue bound to the TSA and SAHA inhibitors. Nature. 1999;401:188–193. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen T.K., Hildmann C., Dickmanns A., Schwienhorst A., Ficner R. Crystal structure of a bacterial class 2 histone deacetylase homologue. J. Mol. Biol. 2005;354:107–120. - PubMed
-
- Sternson S.M., Wong J.C., Grozinger C.M., Schreiber S.L. Synthesis of 7200 small molecules based on a substructural analysis of the histone deacetylase inhibitors trichostatin and trapoxin. Org. Lett. 2001;3:4239–4242. - PubMed
-
- Jenuwein T., Allis C.D. Translating the histone code. Science. 2001;293:1074–1080. - PubMed
-
- Hassig C.A., Schreiber S.L. Nuclear histone acetylases and deacetylases and transcriptional regulation: HATs off to HDACs. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1997;1:300–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

