In Vitro and In Vivo Antitumor Effect of Anti-CD33 Chimeric Receptor-Expressing EBV-CTL against CD33 Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 22272203
- PMCID: PMC3261457
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/683065
In Vitro and In Vivo Antitumor Effect of Anti-CD33 Chimeric Receptor-Expressing EBV-CTL against CD33 Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
Genetic engineering of T cells with chimeric T-cell receptors (CARs) is an attractive strategy to treat malignancies. It extends the range of antigens for adoptive T-cell immunotherapy, and major mechanisms of tumor escape are bypassed. With this strategy we redirected immune responses towards the CD33 antigen to target acute myeloid leukemia. To improve in vivo T-cell persistence, we modified human Epstein Barr Virus-(EBV-) specific cytotoxic T cells with an anti-CD33.CAR. Genetically modified T cells displayed EBV and HLA-unrestricted CD33 bispecificity in vitro. In addition, though showing a myeloablative activity, they did not irreversibly impair the clonogenic potential of normal CD34(+) hematopoietic progenitors. Moreover, after intravenous administration into CD33(+) human acute myeloid leukemia-bearing NOD-SCID mice, anti-CD33-EBV-specific T cells reached the tumor sites exerting antitumor activity in vivo. In conclusion, targeting CD33 by CAR-modified EBV-specific T cells may provide additional therapeutic benefit to AML patients as compared to conventional chemotherapy or transplantation regimens alone.
Figures

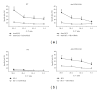
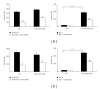

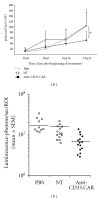

References
-
- Kowolik CM, Topp MS, Gonzalez S, et al. CD28 costimulation provided through a CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptor enhances in vivo persistence and antitumor efficacy of adoptively transferred T cells. Cancer Research. 2006;66(22):10995–11004. - PubMed
-
- Pieper M, Scheffold C, Duwe S, et al. Immunotherapy of B-cell malignancies with genetically engineered human CD8+ natural killer T cells. Leukemia. 2006;20(4):729–732. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed N, Ratnayake M, Savoldo B, et al. Regression of experimental medulloblastoma following transfer of HER2-specific T cells. Cancer Research. 2007;67(12):5957–5964. - PubMed
-
- Faulkner GC, Krajewski AS, Crawford DH. The ins and outs of EBV infection. Trends in Microbiology. 2000;8(4):185–189. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

