Expression of Four Methionine Sulfoxide Reductases in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 22272204
- PMCID: PMC3261475
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/719594
Expression of Four Methionine Sulfoxide Reductases in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
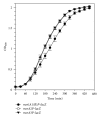
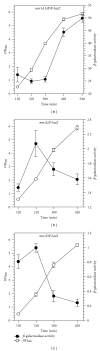
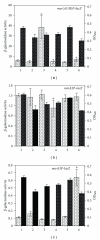
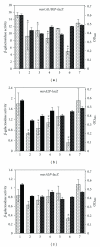
Staphylococcus aureus possesses three MsrA enzymes (MsrA1, MsrA2, MsrA3) that reduce the S-epimer of methionine sulfoxide (MetO) and an MsrB enzyme that reduces R-MetO. The four msr genes are expressed from three different promoters. The msrA1/msrB genes are coexpressed. To determine the expression pattern of msr genes, three independent reporter strains were constructed where msr promoter was cloned in front of a promoterless lacZ and the resulting construct was integrated in the chromosome. Using these strains, it was determined that the msrA1/B expression is significantly higher in S. aureus compared to msrA2 or msrA3. Expression of msrA1/B was highest during stationary phase growth, but the expression of msrA2 and msrA3 was highest during the early to midexponential growth phase. Expression of msrA1/B was induced by oxacillin and the expression of msrA3 was upregulated by salt. Expression of msrA2 remained unchanged under all tested conditions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Methionine Sulfoxide Reductases in Oxidative Stress Tolerance and Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus and Other Bacteria.Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Sep 28;7(10):128. doi: 10.3390/antiox7100128. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30274148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of four methionine sulfoxide reductases in Staphylococcus aureus.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 13;10(2):e0117594. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117594. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25680075 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple methionine sulfoxide reductase genes in Staphylococcus aureus: expression of activity and roles in tolerance of oxidative stress.Microbiology (Reading). 2003 Oct;149(Pt 10):2739-2747. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26442-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2003. PMID: 14523107
-
Regulation of Expression of Oxacillin-Inducible Methionine Sulfoxide Reductases in Staphylococcus aureus.Int J Microbiol. 2015;2015:617925. doi: 10.1155/2015/617925. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Int J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26483841 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of methionine suldfoxide reductases in antioxidant defense, protein regulation and survival.Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(11):1451-7. doi: 10.2174/1381612053507846. Curr Pharm Des. 2005. PMID: 15853675 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Methionine Sulfoxide Reductases in Oxidative Stress Tolerance and Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus and Other Bacteria.Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Sep 28;7(10):128. doi: 10.3390/antiox7100128. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30274148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methionine sulfoxide reductases protect against oxidative stress in Staphylococcus aureus encountering exogenous oxidants and human neutrophils.J Innate Immun. 2014;6(3):353-64. doi: 10.1159/000355915. Epub 2013 Nov 15. J Innate Immun. 2014. PMID: 24247266 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Response Analysis of Escherichia coli to Palladium Stress.Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 8;12:741836. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.741836. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34690987 Free PMC article.
-
Methionine Residues in Exoproteins and Their Recycling by Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase AB Serve as an Antioxidant Strategy in Bacillus cereus.Front Microbiol. 2017 Jul 26;8:1342. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01342. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28798727 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus Peptide Methionine Sulfoxide Reductases Protect from Human Whole-Blood Killing.Infect Immun. 2021 Jul 15;89(8):e0014621. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00146-21. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Infect Immun. 2021. PMID: 34001560 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bamberger DM, Boyd SE. Management of Staphylococcus aureus infections. American Family Physician. 2005;72(12):2474–2481. - PubMed
-
- Lowy FD. Medical progress: staphylococcus aureus infections. New England Journal of Medicine. 1998;339(8):520–532. - PubMed
-
- Murray P, Rosenthal KS, Pfaller M. Medical Microbiology. 5th edition. Philadelphia, Pa, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2002.
-
- Coico R, Sunshine G. Immunology: A Short Course. 6th edition. Hoboken, NJ, USA: Wiley-Blackwell; 2009.
-
- Cabiscol E, Tamarit J, Ros J. Oxidative stress in bacteria and protein damage by reactive oxygen species. International Microbiology. 2000;3(1):3–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

