HERC6 is the main E3 ligase for global ISG15 conjugation in mouse cells
- PMID: 22272257
- PMCID: PMC3260183
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029870
HERC6 is the main E3 ligase for global ISG15 conjugation in mouse cells
Abstract
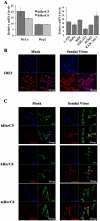
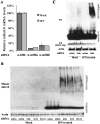
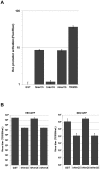
Type I interferon (IFN) stimulates expression and conjugation of the ubiquitin-like modifier IFN-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15), thereby restricting replication of a wide variety of viruses. Conjugation of ISG15 is critical for its antiviral activity in mice. HECT domain and RCC1-like domain containing protein 5 (HerC5) mediates global ISGylation in human cells, whereas its closest relative, HerC6, does not. So far, the requirement of HerC5 for ISG15-mediated antiviral activity has remained unclear. One of the main obstacles to address this issue has been that no HerC5 homologue exists in mice, hampering the generation of a good knock-out model. However, mice do express a homologue of HerC6 that, in contrast to human HerC6, can mediate ISGylation.Here we report that the mouse HerC6 N-terminal RCC1-like domain (RLD) allows ISG15 conjugation when replacing the corresponding domain in the human HerC6 homologue. In addition, sequences in the C-terminal HECT domain of mouse HerC6 also appear to facilitate efficient ISGylation. Mouse HerC6 paralleled human HerC5 in localization and IFN-inducibility. Moreover, HerC6 knock-down in mouse cells abolished global ISGylation, whereas its over expression enhanced the IFNβ promoter and conferred antiviral activity against vesicular stomatitis virus and Newcastle disease virus. Together these data indicate that HerC6 is likely the functional counterpart of human HerC5 in mouse cells, suggesting that HerC6(-/-) mice may provide a feasible model to study the role of human HerC5 in antiviral responses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Murine Herc6 Plays a Critical Role in Protein ISGylation In Vivo and Has an ISGylation-Independent Function in Seminal Vesicles.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015 May;35(5):351-8. doi: 10.1089/jir.2014.0113. Epub 2014 Nov 19. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015. PMID: 25406959 Free PMC article.
-
HERC5 is an IFN-induced HECT-type E3 protein ligase that mediates type I IFN-induced ISGylation of protein targets.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jul 11;103(28):10735-40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600397103. Epub 2006 Jun 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16815975 Free PMC article.
-
Covalent ISG15 conjugation positively regulates the ubiquitin E3 ligase activity of parkin.Open Biol. 2016 Aug;6(8):160193. doi: 10.1098/rsob.160193. Open Biol. 2016. PMID: 27534820 Free PMC article.
-
HERC5 and the ISGylation Pathway: Critical Modulators of the Antiviral Immune Response.Viruses. 2021 Jun 9;13(6):1102. doi: 10.3390/v13061102. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34207696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The antiviral activities of ISG15.J Mol Biol. 2013 Dec 13;425(24):4995-5008. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.09.041. Epub 2013 Oct 3. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24095857 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stimulation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity by Using Filamentous Bacteriophage fd Targeted to DEC-205.J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:585078. doi: 10.1155/2015/585078. Epub 2015 Aug 26. J Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26380324 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Profiling of the Adaptive and Innate Immune Responses of Atlantic Salmon to Renibacterium salmoninarum Infection.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 28;11:567838. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.567838. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33193341 Free PMC article.
-
HERC6 regulates STING activity in a sex-biased manner through modulation of LATS2/VGLL3 Hippo signaling.iScience. 2024 Jan 23;27(2):108986. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.108986. eCollection 2024 Feb 16. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38327798 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale gene co-expression network as a source of functional annotation for cattle genes.BMC Genomics. 2016 Nov 2;17(1):846. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3176-2. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27806696 Free PMC article.
-
IRF3 reduces adipose thermogenesis via ISG15-mediated reprogramming of glycolysis.J Clin Invest. 2021 Apr 1;131(7):e144888. doi: 10.1172/JCI144888. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33571167 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dastur A, Beaudenon S, Kelley M, Krug RM, Huibregtse JM. Herc5, an interferon-induced HECT E3 enzyme, is required for conjugation of ISG15 in human cells. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2006;281:4334–4338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

