Wogonin improves histological and functional outcomes, and reduces activation of TLR4/NF-κB signaling after experimental traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 22272328
- PMCID: PMC3260265
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030294
Wogonin improves histological and functional outcomes, and reduces activation of TLR4/NF-κB signaling after experimental traumatic brain injury
Erratum in
-
Correction: Wogonin Improves Histological and Functional Outcomes, and Reduces Activation of TLR4/NF-κB Signaling after Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury.PLoS One. 2012 Dec 3;7(12):10.1371/annotation/1f110857-27d7-4e83-9eb3-4e5f51950a26. doi: 10.1371/annotation/1f110857-27d7-4e83-9eb3-4e5f51950a26. eCollection 2012. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 29161739 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) initiates a neuroinflammatory cascade that contributes to neuronal damage and behavioral impairment. This study was undertaken to investigate the effects of wogonin, a flavonoid with potent anti-inflammatory properties, on functional and histological outcomes, brain edema, and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)- and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB)-related signaling pathways in mice following TBI.
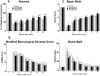
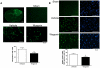
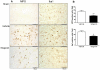
Methodology/principal findings: Mice subjected to controlled cortical impact injury were injected with wogonin (20, 40, or 50 mg·kg(-1)) or vehicle 10 min after injury. Behavioral studies, histology analysis, and measurement of blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability and brain water content were carried out to assess the effects of wogonin. Levels of TLR4/NF-κB-related inflammatory mediators were also examined. Treatment with 40 mg·kg(-1) wogonin significantly improved functional recovery and reduced contusion volumes up to post-injury day 28. Wogonin also significantly reduced neuronal death, BBB permeability, and brain edema beginning at day 1. These changes were associated with a marked reduction in leukocyte infiltration, microglial activation, TLR4 expression, NF-κB translocation to nucleus and its DNA binding activity, matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity, and expression of inflammatory mediators, including interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, macrophage inflammatory protein-2, and cyclooxygenase-2.
Conclusions/significance: Our results show that post-injury wogonin treatment improved long-term functional and histological outcomes, reduced brain edema, and attenuated the TLR4/NF-κB-mediated inflammatory response in mouse TBI. The neuroprotective effects of wogonin may be related to modulation of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

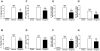

Similar articles
-
Simvastatin reduces secondary brain injury caused by cortical contusion in rats: possible involvement of TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway.Exp Neurol. 2009 Apr;216(2):398-406. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.12.019. Epub 2009 Jan 7. Exp Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19166837
-
Baincalein alleviates early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats: possible involvement of TLR4/NF-κB-mediated inflammatory pathway.Brain Res. 2015 Jan 12;1594:245-55. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.10.014. Epub 2014 Oct 17. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25451085
-
Berberine protects against neuronal damage via suppression of glia-mediated inflammation in traumatic brain injury.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 29;9(12):e115694. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115694. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25546475 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of wogonin in the treatment of central nervous system and degenerative diseases.Brain Res Bull. 2025 Feb;221:111202. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2025.111202. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Brain Res Bull. 2025. PMID: 39814324 Review.
-
Regulation of cell signaling pathways by Wogonin in different cancers: Mechanistic review.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2021 Sep 29;67(2):1-7. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2021.67.2.1. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2021. PMID: 34817345 Review.
Cited by
-
Apolipoprotein E4 impairs spontaneous blood brain barrier repair following traumatic brain injury.Mol Neurodegener. 2018 Apr 4;13(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13024-018-0249-5. Mol Neurodegener. 2018. PMID: 29618365 Free PMC article.
-
Wogonin suppresses inflammatory response and maintains intestinal barrier function via TLR4-MyD88-TAK1-mediated NF-κB pathway in vitro.Inflamm Res. 2015 Jun;64(6):423-31. doi: 10.1007/s00011-015-0822-0. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Inflamm Res. 2015. PMID: 25917044
-
High-dose wogonin exacerbates DSS-induced colitis by up-regulating effector T cell function and inhibiting Treg cell.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Feb;21(2):286-298. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12964. Epub 2016 Sep 19. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 27641629 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of behavioral interventions in traumatic brain injury.Surg Neurol Int. 2024 Jan 26;15:22. doi: 10.25259/SNI_776_2023. eCollection 2024. Surg Neurol Int. 2024. PMID: 38344079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wogonin induces reactive oxygen species production and cell apoptosis in human glioma cancer cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(8):9877-9892. doi: 10.3390/ijms13089877. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22949836 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morganti-Kossmann MC, Rancan M, Stahel PF, Kossmann T. Inflammatory response in acute traumatic brain injury: a double-edged sword. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2002;8:101–105. - PubMed
-
- Dong XQ, Yu WH, Hu YY, Zhang ZY, Huang M. Oxymatrine reduces neuronal cell apoptosis by inhibiting Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor kappa-B-dependent inflammatory responses in traumatic rat brain injury. Inflamm Res. 2011;60:533–539. - PubMed
-
- Chen G, Shi J, Jin W, Wang L, Xie W, et al. Progesterone administration modulates TLRs/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in rat brain after cortical contusion. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2008;38:65–74. - PubMed
-
- Chen G, Zhang S, Shi J, Ai J, Qi M, et al. Simvastatin reduces secondary brain injury caused by cortical contusion in rats: possible involvement of TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. Exp Neurol. 2009;216:398–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

