A new application of lipid nanoemulsions as coating agent, providing zero-order hydrophilic drug release from tablets
- PMID: 22272376
- PMCID: PMC3261482
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/271319
A new application of lipid nanoemulsions as coating agent, providing zero-order hydrophilic drug release from tablets
Abstract
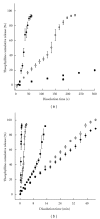
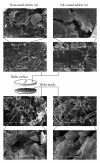
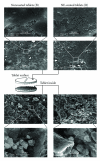
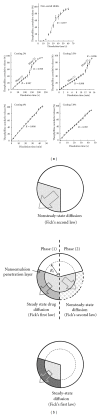
The objective of the present investigation was to evaluate potential of nanoemulsions as a coating material for the tablets. The nanoemulsion of size less than 100 nm was prepared using a simple and low-energy spontaneous emulsification method. Conventional tablets containing theophylline as a model hydrophilic drug were prepared. The theophylline tablets were coated with the nanoemulsion using a fluid bed coater. The effect of different levels of the nanoemulsion coating on the theophylline release was evaluated. The theophylline tablets containing different levels of the nanoemulsion coating could be successfully prepared. Interestingly, the coating of tablet with the nanoemulsion resulted in zero-order release of theophylline from the tablets. The noncoated theophylline tablets release the entire drug in less than 2 minutes, whereas nanoemulsion coating delayed the release of theophylline from tablets. This investigation establishes the proof of concept for the potential of nanoemulsions as a coating material for tablets.
Figures


References
-
- Kim CJ, Lee PI. Hydrophobic anionic gel beads for swelling-controlled drug delivery. Pharmaceutical Research. 1992;9(2):195–199. - PubMed
-
- Langer R. Drug delivery and targeting. Nature. 1998;392(6679):5–10. - PubMed
-
- Lee B, Ryu S, Cui J. Controlled release of dual drug-loaded hydroxypropyl methylcellulose matrix tablet using drug-containing polymeric coatings. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 1999;188:71–80. - PubMed
-
- Torchilin VP. Structure and design of polymeric surfactant-based drug delivery systems. Journal of Controlled Release. 2001;73(2-3):137–172. - PubMed
-
- Lecomte F, Siepmann J, Walther M, MacRae RJ, Bodmeier R. Blends of enteric and GIT-insoluble polymers used for film coating: physicochemical characterization and drug release patterns. Journal of Controlled Release. 2003;89(3):457–471. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

