Speciation of arsenic trioxide metabolites in peripheral blood and bone marrow from an acute promyelocytic leukemia patient
- PMID: 22272800
- PMCID: PMC3293031
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8722-5-1
Speciation of arsenic trioxide metabolites in peripheral blood and bone marrow from an acute promyelocytic leukemia patient
Abstract
Background: Speciation of arsenic trioxide (ATO) metabolites in clinical samples such as peripheral blood (PB) from acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) patients has been conducted. However, speciation of arsenicals in bone marrow (BM) has not yet been performed. Profiles of arsenic speciation in plasma of BM were thus investigated and compared with those of PB plasma from a relapsed APL patient. The total arsenic concentrations in high molecular weight fraction (HMW-F) of BM and PB plasma were also determined.
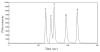
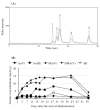
Methods: Response assessment was evaluated by BM aspirate examination and fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis. The analyses of total arsenic concentrations and speciation were preformed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)/ICP-MS, respectively.
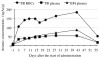
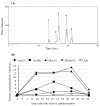
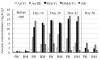
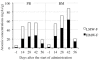
Results: Response assessment showed that the patient achieved complete remission. The total arsenic concentrations in BM plasma increased with time during the consecutive administration. The PB plasma concentrations of methylated arsenic metabolites substantially increased after the start of administration, while those of inorganic arsenic were still kept at a low level, followed by substantially increase from day-14 after administration. The arsenic speciation profiles of PB plasma were very similar to those of BM plasma. Furthermore, the total arsenic concentrations of HMW-F in BM plasma were much higher than those in PB plasma.
Conclusions: The behaviors of arsenic speciation suggested for the first time that arsenic speciation analysis of PB plasma could be predicative for BM speciation, and showed relatively higher efficiency of drug metabolism in the patient. These results may further provide not only significance of clinical application of ATO, but also a new insight into host defense mechanisms in APL patients undergoing ATO treatment, since HMW proteins-bound arsenic complex could be thought to protect BM from the attack of free arsenic species.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Speciation of arsenic trioxide metabolites in blood cells and plasma of a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009 Jan;393(2):689-97. doi: 10.1007/s00216-008-2487-9. Epub 2008 Nov 14. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009. PMID: 19009285
-
Arsenic speciation in saliva of acute promyelocytic leukemia patients undergoing arsenic trioxide treatment.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013 Feb;405(6):1903-11. doi: 10.1007/s00216-012-6700-5. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013. PMID: 23318765 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of arsenic metabolites in patients with newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with arsenic trioxide.Leuk Lymphoma. 2013 Sep;54(9):2041-6. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2013.769222. Epub 2013 Mar 4. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013. PMID: 23343178
-
Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic compounds: in vitro and in vivo studies.Semin Hematol. 2001 Jan;38(1):26-36. doi: 10.1053/shem.2001.20863. Semin Hematol. 2001. PMID: 11172537 Review.
-
Acute promyelocytic leukemia: recent advances in therapy and molecular basis of response to arsenic therapies.Curr Opin Hematol. 2005 Jan;12(1):1-6. doi: 10.1097/01.moh.0000148552.93303.45. Curr Opin Hematol. 2005. PMID: 15604884 Review.
Cited by
-
Old dog, new trick: Trivalent arsenic as an immunomodulatory drug.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 May;177(10):2199-2214. doi: 10.1111/bph.15011. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32022256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significant Association Between the MiR146a Genotypes and Susceptibility to Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Taiwan.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2020 Mar-Apr;17(2):175-180. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20178. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 32108040 Free PMC article.
-
The pharmacokinetics of therapeutic arsenic trioxide in acute promyelocytic leukemia patients.Leuk Lymphoma. 2022 Mar;63(3):653-663. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2021.1978084. Epub 2021 Oct 25. Leuk Lymphoma. 2022. PMID: 34689693 Free PMC article.
-
Chemopreventive and anticancer activity of flavonoids and its possibility for clinical use by combining with conventional chemotherapeutic agents.Am J Cancer Res. 2019 Aug 1;9(8):1517-1535. eCollection 2019. Am J Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31497340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association Between the miR-146a Rs2910164 Polymorphism and Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Susceptibility in an Asian Population.Front Genet. 2020 Oct 2;11:886. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00886. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33133124 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soignet SL, Maslak P, Wang ZG, Jhanwar S, Calleja E, Dardashti LJ, Corso D, DeBlasio A, Gabrilove J, Scheinberg DA, Pandolfi PP, Warrell RP Jr. Complete remission after treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic trioxide. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1341–1348. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199811053391901. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fang J, Chen SJ, Tong JH, Wang ZG, Chen GQ, Chen Z. Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with ATRA and As2O3: a model of molecular target-based cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther. 2002;1:614–620. - PubMed
-
- Melnick A, Licht JD. Deconstructing a disease: RARalpha, its fusion partners, and their roles in the pathogenesis of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 1999;93:3167–3215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

