Generation of anti-human DEC205/CD205 monoclonal antibodies that recognize epitopes conserved in different mammals
- PMID: 22273672
- PMCID: PMC3324822
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jim.2011.12.009
Generation of anti-human DEC205/CD205 monoclonal antibodies that recognize epitopes conserved in different mammals
Abstract
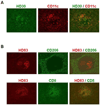
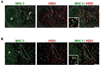
DEC205/CD205 is a C-type multilectin receptor, expressed highly in dendritic cells (DCs). Previous efforts to generate anti-human DEC205 (anti-hDEC205) monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) from mice immunized with subdomain proteins of hDEC205 resulted in a few mAbs. Recently, we expressed and utilized a full-length extracellular domain protein of hDEC205 to successfully generate 5 strong anti-hDEC205 mAbs from mice. In this study, DEC205 knockout (KO) mice were immunized with this full-length extracellular domain protein of hDEC205. One of the 3 immunized DEC205 KO mice was chosen for the highest anti-hDEC205 titer by flow cytometric analysis of serum samples on CHO cells stably expressing hDEC205 (CHO/hDEC205 cells) and used for hybridoma fusion. From a single fusion, more than 400 anti-hDEC205 hybridomas were identified by flow cytometric screen with CHO/hDEC205 cells, and a total of 115 hybridomas secreting strong anti-hDEC205 mAb were saved and named HD1 through HD115. To characterize in detail, 10 HD mAbs were chosen for superior anti-hDEC205 reactivity and further subjected to cloning and purification. Interestingly, out of those 10 chosen anti-hDEC205 HD mAbs, 5 mAbs were also strongly reactive to mouse DEC205 while 8 mAbs were found to stain DEC205(+) DCs on monkey spleen sections. In addition, we also identified that HD83, one of the 10 chosen HD mAbs, stains DEC205(+) DCs in rat spleen and lymph node. Therefore, by immunizing DEC205 KO mice with a full-length extracellular domain protein of hDEC205, we generated a large number of strong anti-hDEC205 mAbs many of which are cross-species reactive and able to visualize DEC205(+) DCs in lymphoid tissues of other mammals.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

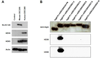
References
-
- Bonifaz L, Bonnyay D, Mahnke K, Rivera M, Nussenzweig MC, Steinman RM. Efficient targeting of protein antigen to the dendritic cell receptor DEC-205 in the steady state leads to antigen presentation on major histocompatibility complex class I products and peripheral CD8+ T cell tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 2002;196:1627. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheong C, Choi JH, Vitale L, He LZ, Trumpfheller C, Bozzacco L, Do Y, Nchinda G, Park SH, Dandamudi DB, Shrestha E, Pack M, Lee HW, Keler T, Steinman RM, Park CG. Improved cellular and humoral immune responses in vivo following targeting of HIV Gag to dendritic cells within human anti-human DEC205 monoclonal antibody. Blood. 2010b;116:3828. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

