An implantable MEMS micropump system for drug delivery in small animals
- PMID: 22273985
- PMCID: PMC3348997
- DOI: 10.1007/s10544-011-9625-4
An implantable MEMS micropump system for drug delivery in small animals
Abstract
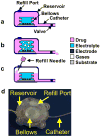
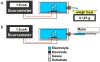
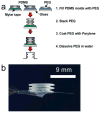
We present the first implantable drug delivery system for controlled timing and location of dosing in small animals. Current implantable drug delivery devices do not provide control over these factors nor are they feasible for implantation in research animals as small as mice. Our system utilizes an integrated electrolysis micropump, is refillable, has an inert drug reservoir for broad drug compatibility, and is capable of adjustment to the delivery regimen while implanted. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was used for characterization of electrodes on glass substrate and a flexible Parylene substrate. Benchtop testing of the electrolysis actuator resulted in flow rates from 1 μL/min to 34 μL/min on glass substrate and up to 6.8 μL/min on Parylene substrate. The fully integrated system generated a flow rate of 4.72 ± 0.35 μL/min under applied constant current of 1.0 mA while maintaining a power consumption of only ~3 mW. Finally, we demonstrated in vivo application of the system for anti-cancer drug delivery in mice.
Figures










References
-
- Alzet. [Accessed October 19, 2011a];ALZET® Osmotic Pumps - Implantable pumps for research. Available at: http://www.alzet.com/
-
- Ambati J, et al. Transscleral delivery of bioactive protein to the choroid and retina. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science. 2000;41(5):1186–1191. - PubMed
-
- Amirouche F, Zhou Y, Johnson T. Current micropump technologies and their biomedical applications. Microsystem Technologies. 2009;15:647–666.
-
- Bard A. Electrochemical methods: fundamentals and applications. 2. New York: Wiley; 2001.
-
- Belmont C, Girault HH. Coplanar interdigitated band electrodes for synthesis Part I: Ohmic loss evaluation. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry. 1994;24:475–480.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

