Cytochrome-c mediated a bystander response dependent on inducible nitric oxide synthase in irradiated hepatoma cells
- PMID: 22274409
- PMCID: PMC3305951
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.9
Cytochrome-c mediated a bystander response dependent on inducible nitric oxide synthase in irradiated hepatoma cells
Abstract
Background: Radiation-induced bystander effect (RIBE) has important implication in tumour radiotherapy, but the bystander signals are still not well known.
Methods: The role of cytochrome-c (cyt-c) and free radicals in RIBE on human hepatoma cells HepG2 was investigated by detecting the formation of bystander micronuclei (MN) and the generation of endogenous cyt-c, inducible nitric oxide (NO) synthase (iNOS), NO, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) molecules.
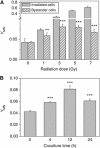
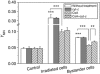
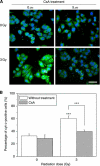
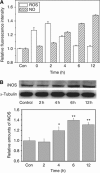
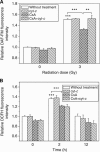
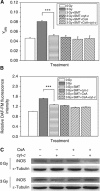
Results: When HepG2 cells were cocultured with an equal number of irradiated HepG2 cells, the yield of MN in the nonirradiated bystander cells was increased in a manner depended on radiation dose and cell coculture time, but it was diminished when the cells were treated with cyclosporin A (CsA), an inhibitor of cyt-c release. Meanwhile the CsA treatment inhibited radiation-induced NO but not ROS. Both of the depressed bystander effect and NO generation in the CsA-treated cells were reversed when 5 μM cyt-c was added in the cell coculture medium. But these exogenous cyt-c-mediated overproductions of NO and bystander MN were abolished when the cells were pretreated with s-methylisothiourea sulphate, an iNOS inhibitor.
Conclusion: Radiation-induced cyt-c has a profound role in regulating bystander response through an iNOS-triggered NO signal but not ROS in HepG2 cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SirT1 knockdown potentiates radiation-induced bystander effect through promoting c-Myc activity and thus facilitating ROS accumulation.Mutat Res. 2015 Feb;772:23-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2014.12.010. Epub 2015 Jan 3. Mutat Res. 2015. PMID: 25772107
-
Radiation-induced intercellular signaling mediated by cytochrome-c via a p53-dependent pathway in hepatoma cells.Oncogene. 2011 Apr 21;30(16):1947-55. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.567. Epub 2010 Dec 6. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21132005 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha particle-induced bystander effect is mediated by ROS via a p53-dependent SCO2 pathway in hepatoma cells.Int J Radiat Biol. 2013 Dec;89(12):1028-34. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2013.817706. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Int J Radiat Biol. 2013. PMID: 23786650
-
Role of nitric oxide in the radiation-induced bystander effect.Redox Biol. 2015 Dec;6:396-400. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.08.018. Epub 2015 Sep 1. Redox Biol. 2015. PMID: 26355395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Radiation-induced bystander effect: the important part of ionizing radiation response. Potential clinical implications].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2009 Aug 18;63:377-88. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2009. PMID: 19724078 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
The emerging role of exosomes in radiotherapy.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Oct 31;20(1):171. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00986-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 36316715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bystander autophagy mediated by radiation-induced exosomal miR-7-5p in non-targeted human bronchial epithelial cells.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 15;6:30165. doi: 10.1038/srep30165. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27417393 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of SKP2 Inhibits the Radiation-Induced Bystander Effects of Esophageal Carcinoma.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017 Feb 6;14(2):155. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14020155. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28178195 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of HIF-1α in Radiosensitivity and Radiation-Induced Bystander Effects Under Hypoxia.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 25;9:637454. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.637454. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33869184 Free PMC article.
-
Biological response of cancer cells to radiation treatment.Front Mol Biosci. 2014 Nov 17;1:24. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2014.00024. eCollection 2014. Front Mol Biosci. 2014. PMID: 25988165 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asur RS, Thomas RA, Tucker JD (2009) Chemical induction of the bystander effect in normal human lymphoblastoid cells. Mutat Res 676: 11–16 - PubMed
-
- Aykin-Burns N, Slane BG, Liu AT, Owens KM, O’Malley MS, Smith BJ, Domann FE, Spitz DR (2011) Sensitivity to low-dose/low-LET ionizing radiation in mammalian cells harboring mutations in succinate dehydrogenase subunit C is governed by mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species. Radiat Res 175: 150–158 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azzam EI, de Toledo SM, Gooding T, Little JB (1998) Intercellular communication is involved in the bystander regulation of gene expression in human cells exposed to very low fluences of alpha particles. Radiat Res 150: 497–504 - PubMed
-
- Azzam EI, de Toledo SM, Little JB (2004) Stress signaling from irradiated to non-irradiated cells. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 4: 53–64 - PubMed
-
- Azzam EI, de Toledo SM, Waker AJ, Little JB (2000) High and low fluences of alpha-particles induce a G1 checkpoint in human diploid fibroblasts. Cancer Res 60: 2623–2631 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

