Pharmacological targets in the renal peritubular microenvironment: implications for therapy for sepsis-induced acute kidney injury
- PMID: 22274552
- PMCID: PMC3319265
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.01.004
Pharmacological targets in the renal peritubular microenvironment: implications for therapy for sepsis-induced acute kidney injury
Abstract
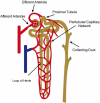
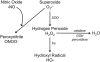
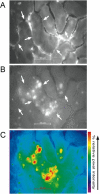
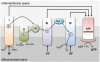
One of the most frequent and serious complications to develop in septic patients is acute kidney injury (AKI), a disorder characterized by a rapid failure of the kidneys to adequately filter the blood, regulate ion and water balance, and generate urine. AKI greatly worsens the already poor prognosis of sepsis and increases cost of care. To date, therapies have been mostly supportive; consequently there has been little change in the mortality rates over the last decade. This is due, at least in part, to the delay in establishing clinical evidence of an infection and the associated presence of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome and thus, a delay in initiating therapy. A second reason is a lack of understanding regarding the mechanisms leading to renal injury, which has hindered the development of more targeted therapies. In this review, we summarize recent studies, which have examined the development of renal injury during sepsis and propose how changes in the peritubular capillary microenvironment lead to and then perpetuate microcirculatory failure and tubular epithelial cell injury. We also discuss a number of potential therapeutic targets in the renal peritubular microenvironment, which may prevent or lessen injury and/or promote recovery.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abrahamson DR, Leardkamolkarn V. Development of kidney tubular basement membranes. Kidney International. 1991;39:382–393. - PubMed
-
- Ader I, Malavaud B, Cuvillier O. When the sphingosine kinase 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate pathway meets hypoxia signaling: new targets for cancer therapy. Cancer Research. 2009;69:3723–3726. - PubMed
-
- Adlam VJ, Harrison JC, Porteous CM, James AM, Smith RA, Murphy MP, Sammut IA. Targeting an antioxidant to mitochondria decreases cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury. FASEB Journal. 2005;19:1088–1095. - PubMed
-
- Al-Mashhadi RH, Skott O, Vanhoutte PM, Hansen PB. Activation of A(2) adenosine receptors dilates cortical efferent arterioles in mouse. Kidney International. 2009;75:793–799. - PubMed
-
- Allende ML, Yamashita T, Proia RL. G-protein-coupled receptor S1P1 acts within endothelial cells to regulate vascular maturation. Blood. 2003;102:3665–3667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

