Combining PET biodistribution and equilibrium dialysis assays to assess the free brain concentration and BBB transport of CNS drugs
- PMID: 22274741
- PMCID: PMC3345915
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2012.1
Combining PET biodistribution and equilibrium dialysis assays to assess the free brain concentration and BBB transport of CNS drugs
Abstract
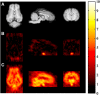
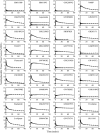
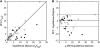
The passage of drugs in and out of the brain is controlled by the blood-brain barrier (BBB), typically, using either passive diffusion across a concentration gradient or active transport via a protein carrier. In-vitro and preclinical measurements of BBB penetration do not always accurately predict the in-vivo situation in humans. Thus, the ability to assay the concentration of novel drug candidates in the human brain in vivo provides valuable information for de-risking of candidate molecules early in drug development. Here, positron emission tomography (PET) measurements are combined with in-vitro equilibrium dialysis assays to enable assessment of transport and estimation of the free brain concentration in vivo. The PET and equilibrium dialysis data were obtained for 36 compounds in the pig. Predicted P-glycoprotein (P-gp) status of the compounds was consistent with the PET/equilibrium dialysis results. In particular, Loperamide, a well-known P-gp substrate, exhibited a significant concentration gradient consistent with active efflux and after inhibition of the P-gp process the gradient was removed. The ability to measure the free brain concentration and assess transport of novel compounds in the human brain with combined PET and equilibrium dialysis assays can be a useful tool in central nervous system (CNS) drug development.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PET Studies on P-glycoprotein function in the blood-brain barrier: how it affects uptake and binding of drugs within the CNS.Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(13):1493-503. doi: 10.2174/1381612043384736. Curr Pharm Des. 2004. PMID: 15134571 Review.
-
P-glycoprotein function at the blood-brain barrier imaged using 11C-N-desmethyl-loperamide in monkeys.J Nucl Med. 2009 Jan;50(1):108-15. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.108.056226. Epub 2008 Dec 17. J Nucl Med. 2009. PMID: 19091890 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging the impact of cyclosporin A and dipyridamole on P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) function at the blood-brain barrier: A [(11)C]-N-desmethyl-loperamide PET study in nonhuman primates.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2016 Aug 25;91:98-104. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2016.06.005. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2016. PMID: 27283486
-
Retrospective analysis of P-glycoprotein-mediated drug-drug interactions at the blood-brain barrier in humans.Drug Metab Dispos. 2013 Apr;41(4):683-8. doi: 10.1124/dmd.112.049577. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013. PMID: 23340958
-
Advances in PET imaging of P-glycoprotein function at the blood-brain barrier.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Feb 20;4(2):225-37. doi: 10.1021/cn3001729. Epub 2012 Dec 4. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23421673 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An evaluation of the brain distribution of [(11)C]GSK1034702, a muscarinic-1 (M 1) positive allosteric modulator in the living human brain using positron emission tomography.EJNMMI Res. 2014 Dec;4(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s13550-014-0066-y. Epub 2014 Dec 5. EJNMMI Res. 2014. PMID: 26116126 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling of PET data in CNS drug discovery and development.J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2013 Jun;40(3):267-79. doi: 10.1007/s10928-013-9320-6. Epub 2013 May 10. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2013. PMID: 23660778 Review.
-
PET in the characterization of immune diseases and development of therapeutics.Oxf Open Immunol. 2025 May 24;6(1):iqaf005. doi: 10.1093/oxfimm/iqaf005. eCollection 2025. Oxf Open Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40584221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of the Brain Biodistribution of the Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) Inhibitor [18F]GSK2647544 in Healthy Male Subjects.Mol Imaging Biol. 2017 Feb;19(1):153-161. doi: 10.1007/s11307-016-0982-5. Mol Imaging Biol. 2017. PMID: 27402093 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetic Modeling of (R)-[11C]verapamil to Measure the P-Glycoprotein Function in Nonhuman Primates.Mol Pharm. 2021 Jan 4;18(1):416-428. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c01014. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Mol Pharm. 2021. PMID: 33315404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abi-Dargham A, Simpson N, Kegeles L, Parsey R, Hwang DR, Anjilvel S, Zea-Ponce Y, Lombardo I, Van HR, Mann JJ, Foged C, Halldin C, Laruelle M. PET studies of binding competition between endogenous dopamine and the D1 radiotracer [11C]NNC 756. Synapse. 1999;32:93–109. - PubMed
-
- Adams KH, Pinborg LH, Svarer C, Hasselbalch SG, Holm S, Haugbøl S, Madsen K, Frøkjær V, Martiny L, Paulson OB, Knudsen GM. A database of [18F]-altanserin binding to 5-HT2A receptors in normal volunteers: normative data and relationship to physiological and demographic variables. Neuroimage. 2004;21:1105–1113. - PubMed
-
- Altman DG, Bland JM. Measurement in medicine: the analysis of method comparison studies. Statistician. 1983;32:307–317.
-
- Borst P, Oude Elferink R. Mammalian ABC transporters in health and disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:537–592. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

