Dietary compounds as potent inhibitors of the signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) 3 regulatory network
- PMID: 22274779
- PMCID: PMC3316753
- DOI: 10.1007/s12263-012-0281-y
Dietary compounds as potent inhibitors of the signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) 3 regulatory network
Abstract
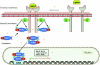
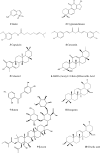
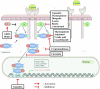
Signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) proteins were described as a family of latent cytosolic transcription factors whose activation is dependent on phosphorylation via growth factor- and cytokine-membrane receptors including interferon and interleukin, or by non-receptor intracellular tyrosine kinases, including Src. A vast majority of natural substances are capable of modulating mitogenic signals, cell survival, apoptosis, cell cycle regulation, angiogenesis as well as processes involved in metastasis development. The inhibition of STAT3 phosphorylation by natural and dietary compounds leads to decreased protein expression of STAT3 targets essentially involved in regulation of the cell cycle and apoptotic cell death. This review details the cell signaling pathways involving STAT transcription factors as well as the corresponding compounds from nature able to interfere with this regulatory system in human cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Constitutive activation of Stat3 by the Src and JAK tyrosine kinases participates in growth regulation of human breast carcinoma cells.Oncogene. 2001 May 3;20(20):2499-513. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204349. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11420660
-
IL-3 signaling and the role of Src kinases, JAKs and STATs: a covert liaison unveiled.Oncogene. 2000 May 15;19(21):2532-47. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203594. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 10851052 Review.
-
Testicular leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and LIF receptor mediate phosphorylation of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT)-3 and STAT-1 and induce c-fos transcription and activator protein-1 activation in rat Sertoli but not germ cells.Endocrinology. 1998 Apr;139(4):1883-90. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.4.5871. Endocrinology. 1998. PMID: 9528974
-
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1/JAB and suppressor of cytokine signaling 3/cytokine-inducible SH2 containing protein 3 negatively regulate the signal transducers and activators of transcription signaling pathway in normal human epidermal keratinocytes.J Invest Dermatol. 2003 Apr;120(4):571-80. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12100.x. J Invest Dermatol. 2003. PMID: 12648219
-
Activated STAT signaling in human tumors provides novel molecular targets for therapeutic intervention.Clin Cancer Res. 2002 Apr;8(4):945-54. Clin Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 11948098 Review.
Cited by
-
STAT3 and STAT5 Targeting for Simultaneous Management of Melanoma and Autoimmune Diseases.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Sep 27;11(10):1448. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101448. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31569642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced tumorigenicity and pathogenicity of cervical carcinoma SiHa cells selected for resistance to cidofovir.Mol Cancer. 2013 Dec 10;12:158. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-158. Mol Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24325392 Free PMC article.
-
Astaxanthin inhibits JAK/STAT-3 signaling to abrogate cell proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis in a hamster model of oral cancer.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 8;9(10):e109114. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109114. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25296162 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid curcumin compounds: a new strategy for cancer treatment.Molecules. 2014 Dec 12;19(12):20839-63. doi: 10.3390/molecules191220839. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 25514225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted inhibition of STATs and IRFs as a potential treatment strategy in cardiovascular disease.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):48788-48812. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9195. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27166190 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alas S, Bonavida B. Rituximab inactivates signal transducer and activation of transcription 3 (STAT3) activity in B-non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma through inhibition of the interleukin 10 autocrine/paracrine loop and results in down-regulation of Bcl-2 and sensitization to cytotoxic drugs. Cancer Res. 2001;61:5137–5144. - PubMed
-
- Arguello F, Alexander M, Sterry JA, Tudor G, Smith EM, Kalavar NT, Greene JF, Jr, Koss W, Morgan CD, Stinson SF, Siford TJ, Alvord WG, Klabansky RL, Sausville EA. Flavopiridol induces apoptosis of normal lymphoid cells, causes immunosuppression, and has potent antitumor activity in vivo against human leukemia and lymphoma xenografts. Blood. 1998;91:2482–2490. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

