Effects of oestrogen on microRNA expression in hormone-responsive breast cancer cells
- PMID: 22274890
- PMCID: PMC10358138
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-012-0102-1
Effects of oestrogen on microRNA expression in hormone-responsive breast cancer cells
Abstract
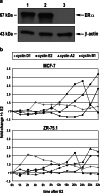
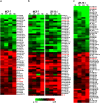
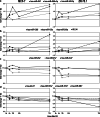
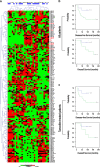
Oestrogen receptor alpha (ERα) is a ligand-dependent transcription factor that mediates oestrogen effects in hormone-responsive cells. Following oestrogenic activation, ERα directly regulates the transcription of target genes via DNA binding. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) represent a class of small noncoding RNAs that function as negative regulators of protein-coding gene expression. They are found aberrantly expressed or mutated in cancer, suggesting their crucial role as either oncogenes or tumour suppressor genes. Here, we analysed changes in miRNA expression in response to oestrogen in hormone-responsive breast cancer MCF-7 and ZR-75.1 cells by microarray-mediated expression profiling. This led to the identification of 172 miRNAs up- or down-regulated by ERα in response to 17β-oestradiol, of which 52 are similarly regulated by the hormone in the two cell models investigated. To identify mechanisms by which ERα exerts its effects on oestrogen-responsive miRNA genes, the oestrogen-dependent miRNA expression profiles were integrated with global in vivo ERα binding site mapping in the genome by ChIP-Seq. In addition, data from miRNA and messenger RNA (mRNA) expression profiles obtained under identical experimental conditions were compared to identify relevant miRNA target transcripts. Results show that miRNAs modulated by ERα represent a novel genomic pathway to impact oestrogen-dependent processes that affect hormone-responsive breast cancer cell behaviour. MiRNome analysis in tumour tissues from breast cancer patients confirmed a strong association between expression of these small RNAs and clinical outcome of the disease, although this appears to involve only marginally the oestrogen-regulated miRNAs identified in this study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Co-regulated gene expression by oestrogen receptor α and liver receptor homolog-1 is a feature of the oestrogen response in breast cancer cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Dec;41(22):10228-40. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt827. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 24049078 Free PMC article.
-
Direct regulation of microRNA biogenesis and expression by estrogen receptor beta in hormone-responsive breast cancer.Oncogene. 2012 Sep 20;31(38):4196-206. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.583. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22231442
-
Estrogen receptor alpha controls a gene network in luminal-like breast cancer cells comprising multiple transcription factors and microRNAs.Am J Pathol. 2010 May;176(5):2113-30. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090837. Epub 2010 Mar 26. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20348243 Free PMC article.
-
Oestrogen-dependent regulation of miRNA biogenesis: many ways to skin the cat.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Aug;40(4):752-8. doi: 10.1042/BST20110763. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 22817728 Review.
-
Small is beautiful: microRNAs and breast cancer-where are we now?J Pathol. 2008 Jul;215(3):214-21. doi: 10.1002/path.2359. J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18446835 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel estrogen-responsive genes (ERGs) for the evaluation of estrogenic activity.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 17;17(8):e0273164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273164. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35976950 Free PMC article.
-
miR-148a-mediated estrogen-induced cholestasis in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: Role of PXR/MRP3.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 2;12(6):e0178702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178702. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28575098 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA Regulation and Its Consequences in Cancer.Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2013 Mar;1(1):71-79. doi: 10.1007/s40139-012-0002-7. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23420713 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in porcine uterus and serum are affected by zearalenone and represent a new target for mycotoxin biomarker discovery.Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 28;9(1):9408. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45784-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31253833 Free PMC article.
-
Estradiol induces apoptosis via activation of miRNA-23a and p53: implication for gender difference in liver cancer development.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 27;6(33):34941-52. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5472. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26439986 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

