C. elegans dystroglycan coordinates responsiveness of follower axons to dorsal/ventral and anterior/posterior guidance cues
- PMID: 22275151
- PMCID: PMC3507465
- DOI: 10.1002/dneu.22011
C. elegans dystroglycan coordinates responsiveness of follower axons to dorsal/ventral and anterior/posterior guidance cues
Abstract
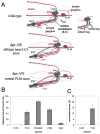
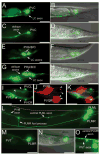
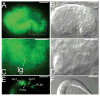
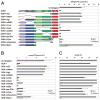
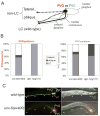
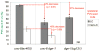
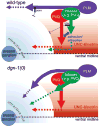
Neural development in metazoans is characterized by the establishment of initial process tracts by pioneer axons and the subsequent extension of follower axons along these pioneer processes. Mechanisms governing the fidelity of follower extension along pioneered routes are largely unknown. In C. elegans, formation of the right angle-shaped lumbar commissure connecting the lumbar and preanal ganglia is an example of pioneer/follower dynamics. We find that the dystroglycan ortholog DGN-1 mediates the fidelity of follower lumbar commissure axon extension along the pioneer axon route. In dgn-1 mutants, the axon of the pioneer PVQ neuron faithfully establishes the lumbar commissure, but axons of follower lumbar neurons, such as PVC, frequently bypass the lumbar commissure and extend along an oblique trajectory directly toward the preanal ganglion. In contrast, disruption of the UNC-6/netrin guidance pathway principally perturbs PVQ ventral guidance to pioneer the lumbar commissure. Loss of DGN-1 in unc-6 mutants has a quantitatively similar effect on follower axon guidance regardless of PVQ axon route, indicating that DGN-1 does not mediate follower/pioneer adhesion. Instead, DGN-1 appears to block premature responsiveness of follower axons to a preanal ganglion-directed guidance cue, which mediates ventral-to-anterior reorientation of lumbar commissure axons. Deletion analysis shows that only the most N-terminal DGN-1 domain is required for these activities. These studies suggest that dystroglycan modulation of growth cone responsiveness to conflicting guidance cues is important for restricting follower axon extension to the tracts laid down by pioneers.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

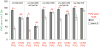
Similar articles
-
The Flamingo ortholog FMI-1 controls pioneer-dependent navigation of follower axons in C. elegans.Development. 2010 Nov;137(21):3663-73. doi: 10.1242/dev.054320. Epub 2010 Sep 28. Development. 2010. PMID: 20876647 Free PMC article.
-
ccd-5, a novel cdk-5 binding partner, regulates pioneer axon guidance in the ventral nerve cord of Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2022 Apr 4;220(4):iyac024. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac024. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 35143653 Free PMC article.
-
wrk-1 and rig-5 control pioneer and follower axon navigation in the ventral nerve cord of Caenorhabditis elegans in a nid-1 mutant background.Genetics. 2023 Mar 2;223(3):iyac187. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac187. Genetics. 2023. PMID: 36573271 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of longitudinal axon pathways in Caenorhabditis elegans.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Jan;85:60-70. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.11.015. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 29141179 Review.
-
Axon guidance: asymmetric signaling orients polarized outgrowth.Trends Cell Biol. 2008 Dec;18(12):597-603. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2008.09.005. Epub 2008 Oct 24. Trends Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18951796 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dystroglycan is a scaffold for extracellular axon guidance decisions.Elife. 2019 Feb 13;8:e42143. doi: 10.7554/eLife.42143. Elife. 2019. PMID: 30758284 Free PMC article.
-
The Genetics of Axon Guidance and Axon Regeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2016 Nov;204(3):849-882. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.186262. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 28114100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural maintenance roles for the matrix receptor dystroglycan and the nuclear anchorage complex in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2012 Apr;190(4):1365-77. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.136184. Epub 2012 Jan 31. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22298703 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akhavan A, Crivelli SN, Singh M, Lingappa VR, Muschler JL. SEA domain proteolysis determines the functional composition of dystroglycan. FASEB J. 2008;22:612–21. - PubMed
-
- Altun-Gultekin Z, Andachi Y, Tsalik EL, Pilgrim D, Kohara Y, Hobert O. A regulatory cascade of three homeobox genes, ceh-10, ttx-3 and ceh-23, controls cell fate specification of a defined interneuron class in C. elegans. Development. 2001;128:1951–69. - PubMed
-
- Aurelio O, Hall DH, Hobert O. Immunoglobulin-domain proteins required for maintenance of ventral nerve cord organization. Science. 2002;295:686–90. - PubMed
-
- Bak M, Fraser SE. Axon fasciculation and differences in midline kinetics between pioneer and follower axons within commissural fascicles. Development. 2003;130:4999–5008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

