Antibody-induced enhancement of factor VIIa activity through distinct allosteric pathways
- PMID: 22275370
- PMCID: PMC3308810
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.312330
Antibody-induced enhancement of factor VIIa activity through distinct allosteric pathways
Abstract
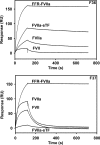
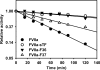
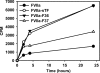
In the absence of its cofactor tissue factor (TF), coagulation factor VIIa (FVIIa) predominantly exists in a zymogen-like, catalytically incompetent state. Here we demonstrate that conformation-specific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) can be used to characterize structural features determining the activity of FVIIa. We isolated two classes of mAbs, which both increased the catalytic efficiency of FVIIa more than 150-fold. The effects of the antibodies were retained with a FVIIa variant, which has been shown to be inert to allosteric activation by the natural activator TF, suggesting that the antibodies and TF employ distinct mechanisms of activation. The antibodies could be classified into two groups based on their patterns of affinities for different conformations of FVIIa. Whereas one class of antibodies affected both the K(m) and k(cat), the other class mainly affected the K(m). The antibody-induced activity enhancement could be traced to maturation of the S1 substrate binding pocket and the oxyanion hole, evident by an increased affinity for p-aminobenzamidine, an increased rate of antithrombin inhibition, an increased rate of incorporation of diisopropylfluorophosphate, and an enhanced fraction of molecules with a buried N terminus of the catalytic domain in the presence of antibodies. As demonstrated by site-directed mutagenesis, the two groups of antibodies appear to have overlapping, although clearly different, epitopes in the 170-loop. Our findings suggest that binding of ligands to specific residues in the 170-loop or its spatial vicinity may stabilize the S1 pocket and the oxyanion hole, and they may have general implications for the molecular understanding of FVIIa regulatory mechanisms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Beating tissue factor at its own game: Design and properties of a soluble tissue factor-independent coagulation factor VIIa.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jan 10;295(2):517-528. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009183. Epub 2019 Dec 4. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31801825 Free PMC article.
-
Activation loop 3 and the 170 loop interact in the active conformation of coagulation factor VIIa.FEBS J. 2009 Jun;276(11):3099-109. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07028.x. Epub 2009 Apr 23. FEBS J. 2009. PMID: 19490111
-
Molecular Basis of Enhanced Activity in Factor VIIa-Trypsin Variants Conveys Insights into Tissue Factor-mediated Allosteric Regulation of Factor VIIa Activity.J Biol Chem. 2016 Feb 26;291(9):4671-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.698613. Epub 2015 Dec 22. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26694616 Free PMC article.
-
Cofactor-induced and mutational activity enhancement of coagulation factor VIIa.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Mar;65(6):953-63. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-7480-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18066494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allosteric activation of coagulation factor VIIa.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011 Jun 1;16(8):3156-63. doi: 10.2741/3903. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011. PMID: 21622226 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms mediating enhanced neutralization efficacy of staphylococcal enterotoxin B by combinations of monoclonal antibodies.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 13;290(11):6715-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.630715. Epub 2015 Jan 8. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25572397 Free PMC article.
-
The spatial structure of cell signaling systems.Phys Biol. 2013 Aug;10(4):045004. doi: 10.1088/1478-3975/10/4/045004. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Phys Biol. 2013. PMID: 23913102 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering of a membrane-triggered activity switch in coagulation factor VIIa.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Nov 21;114(47):12454-12459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1618713114. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 29109275 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davie E. W., Fujikawa K., Kisiel W. (1991) The coagulation cascade. Initiation, maintenance, and regulation. Biochemistry 30, 10363–10370 - PubMed
-
- Pedersen A. H., Nordfang O., Norris F., Wiberg F. C., Christensen P. M., Moeller K. B., Meidahl-Pedersen J., Beck T. C., Norris K., Hedner U., Kisiel W. (1990) Recombinant human extrinsic pathway inhibitor. Production, isolation, and characterization of its inhibitory activity on tissue factor-initiated coagulation reactions. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 16786–16793 - PubMed
-
- Silverberg S. A., Nemerson Y., Zur M. (1977) Kinetics of the activation of bovine coagulation factor X by components of the extrinsic pathway. Kinetic behavior of two-chain factor VII in the presence and absence of tissue factor. J. Biol. Chem. 252, 8481–8488 - PubMed
-
- Monroe D. M., Key N. S. (2007) The tissue factor-factor VIIa complex. Procoagulant activity, regulation, and multitasking. J. Thromb. Haemost. 5, 1097–1105 - PubMed
-
- Higashi S., Nishimura H., Aita K., Iwanaga S. (1994) Identification of regions of bovine factor VII essential for binding to tissue factor. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 18891–18898 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

