Structural basis for Ca2+-induced activation and dimerization of estrogen receptor α by calmodulin
- PMID: 22275375
- PMCID: PMC3308758
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.334797
Structural basis for Ca2+-induced activation and dimerization of estrogen receptor α by calmodulin
Abstract
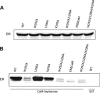
The estrogen receptor α (ER-α) regulates expression of target genes implicated in development, metabolism, and breast cancer. Calcium-dependent regulation of ER-α is critical for activating gene expression and is controlled by calmodulin (CaM). Here, we present the NMR structures for the two lobes of CaM each bound to a localized region of ER-α (residues 287-305). A model of the complete CaM·ER-α complex was constructed by combining these two structures with additional data. The two lobes of CaM both compete for binding at the same site on ER-α (residues 292, 296, 299, 302, and 303), which explains why full-length CaM binds two molecules of ER-α in a 1:2 complex and stabilizes ER-α dimerization. Exposed glutamate residues in CaM (Glu(11), Glu(14), Glu(84), and Glu(87)) form salt bridges with key lysine residues in ER-α (Lys(299), Lys(302), and Lys(303)), which are likely to prevent ubiquitination at these sites and inhibit degradation of ER-α. Mutants of ER-α at the CaM-binding site (W292A and K299A) weaken binding to CaM, and I298E/K299D disrupts estrogen-induced transcription. CaM facilitates dimerization of ER-α in the absence of estrogen, and stimulation of ER-α by either Ca(2+) and/or estrogen may serve to regulate transcription in a combinatorial fashion.
Figures

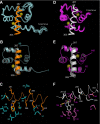
Similar articles
-
A Non-Canonical Calmodulin Target Motif Comprising a Polybasic Region and Lipidated Terminal Residue Regulates Localization.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 15;21(8):2751. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082751. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calmodulin Lobes Facilitate Dimerization and Activation of Estrogen Receptor-α.J Biol Chem. 2017 Mar 17;292(11):4614-4622. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.754804. Epub 2017 Feb 7. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28174300 Free PMC article.
-
Calmodulin-independent, agonistic properties of a peptide containing the calmodulin binding site of estrogen receptor alpha.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007 Mar 30;268(1-2):37-49. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2007.01.012. Epub 2007 Jan 25. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17316976
-
Calmodulin, a regulatory partner of the estrogen receptor alpha in breast cancer cells.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008 Sep 10;291(1-2):20-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2008.04.011. Epub 2008 Apr 26. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18524472 Review.
-
Calcium-calmodulin-induced dimerization of the carboxyl-terminal domain from petunia glutamate decarboxylase. A novel calmodulin-peptide interaction motif.J Biol Chem. 1998 Nov 13;273(46):30328-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.46.30328. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9804795
Cited by
-
IQGAP1 binds to estrogen receptor-α and modulates its function.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 28;289(13):9100-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.553511. Epub 2014 Feb 18. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24550401 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen Enhances Linkage in the Vascular Endothelial Calmodulin Network via a Feedforward Mechanism at the G Protein-coupled Estrogen Receptor 1.J Biol Chem. 2016 May 13;291(20):10805-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.697334. Epub 2016 Mar 17. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26987903 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Na+/H+ exchanger 1 (NHE1) - calmodulin complexes of varying stoichiometry and structure regulate Ca2+-dependent NHE1 activation.Elife. 2021 Mar 3;10:e60889. doi: 10.7554/eLife.60889. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33655882 Free PMC article.
-
A Non-Canonical Calmodulin Target Motif Comprising a Polybasic Region and Lipidated Terminal Residue Regulates Localization.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 15;21(8):2751. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082751. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and thermodynamic characterization of the recognition of the S100-binding peptides TRTK12 and p53 by calmodulin.Protein Sci. 2014 Sep;23(9):1247-61. doi: 10.1002/pro.2506. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Protein Sci. 2014. PMID: 24947426 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hall J. M., Couse J. F., Korach K. S. (2001) The multifaceted mechanisms of estradiol and estrogen receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 36869–36872 - PubMed
-
- Dickson R. B., Stancel G. M. (2000) Estrogen receptor-mediated processes in normal and cancer cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 27, 135–145 - PubMed
-
- McKenna N. J., Lanz R. B., O'Malley B. W. (1999) Nuclear receptor coregulators. Cellular and molecular biology. Endocr. Rev. 20, 321–344 - PubMed
-
- Li L., Li Z., Sacks D. B. (2005) The transcriptional activity of estrogen receptor-α is dependent on Ca2+/calmodulin. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 13097–13104 - PubMed
-
- Li L., Li Z., Sacks D. B. (2003) Calmodulin regulates the transcriptional activity of estrogen receptors. Selective inhibition of calmodulin function in subcellular compartments. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 1195–1200 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

