Combined MEK and VEGFR inhibition in orthotopic human lung cancer models results in enhanced inhibition of tumor angiogenesis, growth, and metastasis
- PMID: 22275507
- PMCID: PMC3306446
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2324
Combined MEK and VEGFR inhibition in orthotopic human lung cancer models results in enhanced inhibition of tumor angiogenesis, growth, and metastasis
Abstract
Purpose: Ras/Raf/mitogen-activated protein-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase (MEK)/ERK signaling is critical for tumor cell proliferation and survival. Selumetinib is a potent, selective, and orally available MEK1/2 inhibitor. In this study, we evaluated the therapeutic efficacy of selumetinib alone or with cediranib, an orally available potent inhibitor of all three VEGF receptor (VEGFR) tyrosine kinases, in murine orthotopic non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) models.
Experimental design: NCI-H441 or NCI-H460 KRAS-mutant human NSCLC cells were injected into the lungs of mice. Mice were randomly assigned to treatment with selumetinib, cediranib, paclitaxel, selumetinib plus cediranib, or control. When controls became moribund, all animals were sacrificed and assessed for lung tumor burden and locoregional metastasis. Lung tumors and adjacent normal tissues were subjected to immunohistochemical analyses.
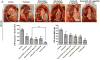
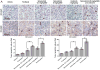
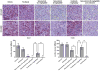
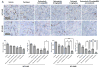
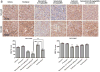
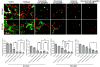
Results: Selumetinib inhibited lung tumor growth and, particularly at higher dose, reduced locoregional metastasis, as did cediranib. Combining selumetinib and cediranib markedly enhanced their antitumor effects, with near complete suppression of metastasis. Immunohistochemistry of tumor tissues revealed that selumetinib alone or with cediranib reduced ERK phosphorylation, angiogenesis, and tumor cell proliferation and increased apoptosis. The antiangiogenic and apoptotic effects were substantially enhanced when the agents were combined. Selumetinib also inhibited lung tumor VEGF production and VEGFR signaling.
Conclusions: In this study, we evaluated therapy directed against MEK combined with antiangiogenic therapy in distinct orthotopic NSCLC models. MEK inhibition resulted in potent antiangiogenic effects with decreased VEGF expression and signaling. Combining selumetinib with cediranib enhanced their antitumor and antiangiogenic effects. We conclude that combining selumetinib and cediranib represents a promising strategy for the treatment of NSCLC.
Figures



Similar articles
-
BYL719, a selective inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-Kinase α, enhances the effect of selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886) in KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer.Invest New Drugs. 2015 Feb;33(1):12-21. doi: 10.1007/s10637-014-0163-9. Epub 2014 Oct 25. Invest New Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25342139
-
Antitumor activity of selective MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 in combination with PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235 in gefitinib-resistant NSCLC xenograft models.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Jun 17;33(1):52. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-33-52. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24939055 Free PMC article.
-
BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis.Cancer Res. 2004 Oct 1;64(19):7099-109. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1443. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15466206
-
Treating non-small cell lung cancer with selumetinib: an up-to-date drug evaluation.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;21(16):1943-1953. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1798930. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32880495 Review.
-
Selumetinib in advanced non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harbouring KRAS mutation: endless clinical challenge to KRAS-mutant NSCLC.Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2013 Jun;8(2):93-100. doi: 10.2174/15748871113089990047. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2013. PMID: 24063423 Review.
Cited by
-
Landscape of Targeted Anti-Cancer Drug Synergies in Melanoma Identifies a Novel BRAF-VEGFR/PDGFR Combination Treatment.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 13;10(10):e0140310. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140310. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26461489 Free PMC article.
-
NF1 deletion generates multiple subtypes of soft-tissue sarcoma that respond to MEK inhibition.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Sep;12(9):1906-17. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0189. Epub 2013 Jul 15. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 23858101 Free PMC article.
-
An orthotopic non-small cell lung cancer model for image-guided small animal radiotherapy platforms.Br J Radiol. 2019 Mar;92(1095):20180476. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180476. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Br J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30465693 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin-like transcript 4 promotes tumor progression and metastasis and up-regulates VEGF-C expression via ERK signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 May 30;6(15):13550-63. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3624. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25948790 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor VEGF:VEGFR2 autocrine feed-forward loop triggers angiogenesis in lung cancer.J Clin Invest. 2013 Apr;123(4):1732-40. doi: 10.1172/JCI65385. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23454747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global Cancer Statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Pao W, Girard N. New driver mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:175–80. - PubMed
-
- Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J, Schiller JH, Dowlati A, et al. Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2542–50. - PubMed
-
- Reck M, von Pawel J, Zatloukal P, Ramlau R, Gorbounova V, Hirsh V, et al. Phase III Trial of Cisplatin Plus Gemcitabine With Either Placebo or Bevacizumab As First-Line Therapy for Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: AVAiL. J Clin Oncol. 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

