P1 and P2 protein heterodimer binding to the P0 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is relatively non-specific and a source of ribosomal heterogeneity
- PMID: 22275522
- PMCID: PMC3378876
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks036
P1 and P2 protein heterodimer binding to the P0 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is relatively non-specific and a source of ribosomal heterogeneity
Abstract
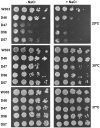
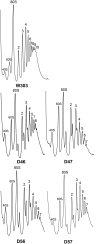
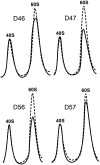
The ribosomal stalk is formed by four acidic phosphoproteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, P1α, P1β, P2α and P2β, which form two heterodimers, P1α/P2β and P1β/P2α, that preferentially bind to sites A and B of the P0 protein, respectively. Using mutant strains carrying only one of the four possible P1/P2 combinations, we found a specific phenotype associated to each P1/P2 pair, indicating that not all acidic P proteins play the same role. The absence of one P1/P2 heterodimer reduced the rate of cell growth by varying degrees, depending on the proteins missing. Synthesis of the 60S ribosomal subunit also decreased, particularly in strains carrying the unusual P1α-P2α or P1β-P2β heterodimers, although the distinct P1/P2 dimers are bound with similar affinity to the mutant ribosome. While in wild-type strains the B site bound P1β/P2α in a highly specific manner and the A site bound the four P proteins similarly, both the A and B binding sites efficiently bound practically any P1/P2 pair in mutant strains expressing truncated P0 proteins. The reported results support that while most ribosomes contain a P1α/P2β-P0-P1β/P2α structure in normal conditions, the stalk assembly mechanism can generate alternative compositions, which have been previously detected in the cell.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vivo formation of a stable pentameric (P2alpha/P1beta)-P0-(P1alpha/P2beta) ribosomal stalk complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Yeast. 2010 Sep;27(9):693-704. doi: 10.1002/yea.1765. Yeast. 2010. PMID: 20225338
-
Asymmetric interactions between the acidic P1 and P2 proteins in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal stalk.J Biol Chem. 2001 Aug 31;276(35):32474-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103229200. Epub 2001 Jun 28. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11431471
-
Characterization of interaction sites in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal stalk components.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Nov;46(3):719-29. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03179.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12410829
-
Structural and functional characterization of the amino terminal domain of the yeast ribosomal stalk P1 and P2 proteins.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Jun;41(6):1315-22. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.11.005. Epub 2008 Nov 25. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19084076
-
Proteins P1, P2, and P0, components of the eukaryotic ribosome stalk. New structural and functional aspects.Biochem Cell Biol. 1995 Nov-Dec;73(11-12):959-68. doi: 10.1139/o95-103. Biochem Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 8722011 Review.
Cited by
-
RPLP2 activates TLR4 in an autocrine manner and promotes HIF-1α-induced metabolic reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Dec 5;9(1):440. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01719-0. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 38052785 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and rates of exchange of L7/L12 between ribosomes and the effects of binding EF-G.ACS Chem Biol. 2012 Jun 15;7(6):1120-7. doi: 10.1021/cb300081s. Epub 2012 Apr 18. ACS Chem Biol. 2012. PMID: 22489843 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal protein and biogenesis factors affect multiple steps during movement of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ty1 retrotransposon.Mob DNA. 2015 Dec 8;6:22. doi: 10.1186/s13100-015-0053-5. eCollection 2015. Mob DNA. 2015. PMID: 26664557 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting RPLP2 Triggers DLBCL Ferroptosis by Decreasing FXN Expression.Biomedicines. 2025 May 28;13(6):1320. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061320. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564039 Free PMC article.
-
RPLP1, an NS4B-interacting protein, enhances production of CSFV through promoting translation of viral genome.Virulence. 2022 Dec;13(1):370-386. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2033500. Virulence. 2022. PMID: 35129423 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballesta JPG, Remacha M. The large ribosomal subunit stalk as a regulatory element of the eukaryotic translational machinery. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1996;55:157–193. - PubMed
-
- Tchorzewski M. The acidic ribosomal P proteins. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002;34:911–915. - PubMed
-
- Huang C, Mandava CS, Sanyal S. The ribosomal stalk plays a key role in IF2-mediated association of the ribosomal subunits. J. Mol. Biol. 2010;399:145–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

