The nucleoid-associated proteins H-NS and FIS modulate the DNA supercoiling response of the pel genes, the major virulence factors in the plant pathogen bacterium Dickeya dadantii
- PMID: 22275524
- PMCID: PMC3378864
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks014
The nucleoid-associated proteins H-NS and FIS modulate the DNA supercoiling response of the pel genes, the major virulence factors in the plant pathogen bacterium Dickeya dadantii
Abstract
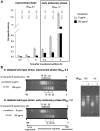
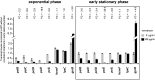
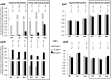
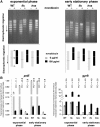
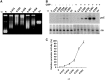
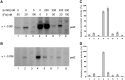
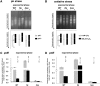
Dickeya dadantii is a pathogen infecting a wide range of plant species. Soft rot, the visible symptom, is mainly due to the production of pectate lyases (Pels) that can destroy the plant cell walls. Previously we found that the pel gene expression is modulated by H-NS and FIS, two nucleoid-associated proteins (NAPs) modulating the DNA topology. Here, we show that relaxation of the DNA in growing D. dadantii cells decreases the expression of pel genes. Deletion of fis aggravates, whereas that of hns alleviates the negative impact of DNA relaxation on pel expression. We further show that H-NS and FIS directly bind the pelE promoter and that the response of D. dadantii pel genes to stresses that induce DNA relaxation is modulated, although to different extents, by H-NS and FIS. We infer that FIS acts as a repressor buffering the negative impact of DNA relaxation on pel gene transcription, whereas H-NS fine-tunes the response of virulence genes precluding their expression under suboptimal conditions of supercoiling. This novel dependence of H-NS effect on DNA topology expands our understanding of the role of NAPs in regulating the global bacterial gene expression and bacterial pathogenicity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of the LysR-type transcriptional regulator PecT and DNA supercoiling in the thermoregulation of pel genes, the major virulence factors in Dickeya dadantii.Environ Microbiol. 2014 Mar;16(3):734-45. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12198. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 23869858
-
Regulation of pel genes, major virulence factors in the plant pathogen bacterium Dickeya dadantii, is mediated by cooperative binding of the nucleoid-associated protein H-NS.Res Microbiol. 2016 May;167(4):247-253. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2016.02.001. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Res Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26912324
-
H-NS-dependent activation of pectate lyases synthesis in the phytopathogenic bacterium Erwinia chrysanthemi is mediated by the PecT repressor.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Feb;43(3):733-48. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02782.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11929528
-
Bacterial virulence and Fis: adapting regulatory networks to the host environment.Trends Microbiol. 2014 Feb;22(2):92-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2013.11.008. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Trends Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24370464 Review.
-
Co-operative roles for DNA supercoiling and nucleoid-associated proteins in the regulation of bacterial transcription.Biochem Soc Trans. 2013 Apr;41(2):542-7. doi: 10.1042/BST20120222. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013. PMID: 23514151 Review.
Cited by
-
The regulation of DNA supercoiling across evolution.Protein Sci. 2021 Oct;30(10):2042-2056. doi: 10.1002/pro.4171. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Protein Sci. 2021. PMID: 34398513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Interplay among FIS, H-NS, and Guanosine Tetraphosphate Modulates Transcription of the Escherichia coli cspA Gene under Physiological Growth Conditions.Front Mol Biosci. 2016 May 24;3:19. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2016.00019. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Biosci. 2016. PMID: 27252944 Free PMC article.
-
Innovation and Application of the Type III Secretion System Inhibitors in Plant Pathogenic Bacteria.Microorganisms. 2020 Dec 9;8(12):1956. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8121956. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33317075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Propionylation of Fis K32 in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi: a key modification affecting pathogenicity.Future Microbiol. 2025 Mar;20(4):295-303. doi: 10.1080/17460913.2025.2460338. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Future Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39885648
-
Early fate of exogenous promoters in E. coli.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Mar 18;48(5):2348-2356. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1196. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31960057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Browning DF, Busby SJ. The regulation of bacterial transcription initiation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004;2:57–65. - PubMed
-
- Travers A, Muskhelishvili G. DNA supercoiling - a global transcriptional regulator for enterobacterial growth? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005;3:157–169. - PubMed
-
- Ishihama A. Prokaryotic genome regulation: multifactor promoters, multitarget regulators and hierarchic networks. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010;34:628–645. - PubMed
-
- Muskhelishvili G, Sobetzko P, Geertz M, Berger M. General organisational principles of the transcriptional regulation system: a tree or a circle? Mol. Biosyst. 2010;6:662–676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

