Evaluation of the levofloxacin release characters from a rabbit foldable capsular vitreous body
- PMID: 22275817
- PMCID: PMC3260945
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S25268
Evaluation of the levofloxacin release characters from a rabbit foldable capsular vitreous body
Abstract
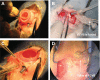
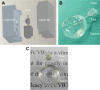
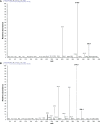
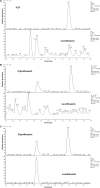
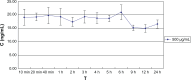
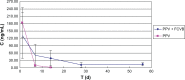
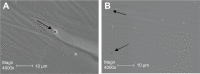
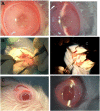
The authors have manufactured a novel rabbit foldable capsular vitreous body (FCVB). The aim of this study was to determine whether this rabbit FCVB can release levofloxacin in vitro and in vivo, and to evaluate the release characteristics. In vitro, the rabbit FCVB with levofloxacin 500 μg/mL was immersed in cups of modified Franz diffusion cells. Following this, 200 μL of liquid was aspirated at intervals from 10 minutes to 24 hours. In vivo, the FCVB with levofloxacin was implanted into the right eyes of five rabbits. After implantation, the aqueous humor was aspirated on days 1, 7, 14, 28, and 56. The levofloxacin concentrations in the cups and aqueous humor samples were detected by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. The FCVB was observed under a scanning electron microscope. The results showed that the released levofloxacin was stabilized at 20 ng/mL at time points from 10 minutes to 24 hours in vitro. In vivo, levofloxacin concentrations in the aqueous humor were 132, 50, 39, 11, and 15 ng/mL on days 1, 7, 14, 28, and 56, respectively. In the FCVB capsules, 300 nm apertures were observed. These results suggest the rabbit FCVB released levofloxacin stably in vitro and sustainably in vivo. This study provides a novel combined approach, with the FCVB as a vitreous substitute and drug delivery system for the treatment of bacterial endophthalmitis.
Keywords: bacterial endophthalmitis; drug delivery system; high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry; vitreous substitute.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of levofloxacin release characteristics from a human foldable capsular vitreous body in vitro.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Feb;28(1):33-40. doi: 10.1089/jop.2011.0109. Epub 2011 Oct 26. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22029539
-
A preliminary study to treat severe endophthalmitis via a foldable capsular vitreous body with sustained levofloxacin release in rabbits.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Jan 28;54(1):804-12. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-9695. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23258145
-
Evaluation of 5-fluorouracil released from a foldable capsular vitreous body in vitro and in vivo.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012 May;250(5):751-9. doi: 10.1007/s00417-011-1862-y. Epub 2011 Nov 27. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012. PMID: 22119880
-
Sustained mechanical release of dexamethasone sodium phosphate from a foldable capsular vitreous body.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Mar;51(3):1636-42. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4134. Epub 2009 Oct 15. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 19834025
-
Penetration of second-, third-, and fourth-generation topical fluoroquinolone into aqueous and vitreous humour in a rabbit endophthalmitis model.Eye (Lond). 2007 Jul;21(7):990-4. doi: 10.1038/sj.eye.6702414. Epub 2006 May 26. Eye (Lond). 2007. PMID: 16732216
Cited by
-
Comprehensive analysis of inflammatory immune mediators of the intraocular fluid aspirated from the foldable capsular vitreous body filled-eyes.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46384. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046384. Epub 2012 Oct 1. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23049699 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A novel vitreous substitute of using a foldable capsular vitreous body injected with polyvinylalcohol hydrogel.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1838. doi: 10.1038/srep01838. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23670585 Free PMC article.
-
Foldable capsular vitreous body implantation for treatment of traumatic retinal detachment: two case reports.J Int Med Res. 2021 Feb;49(2):300060521990257. doi: 10.1177/0300060521990257. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33563057 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the effectiveness and safety of Foldable Capsular Vitreous Body implantation.BMC Ophthalmol. 2019 Dec 18;19(1):260. doi: 10.1186/s12886-019-1268-x. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31852464 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Polysaccharide- and Synthetic Polymer-Based Vitreous Substitutes.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 8;15(2):566. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020566. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839888 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study Group Results of the Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study: a randomized trial of immediate vitrectomy and of intravenous antibiotics for the treatment of postoperative bacterial endophthalmitis. Arch Ophthamol. 1995;113(12):1479–1496. - PubMed
-
- Jackson TL, Eykyn SJ, Graham EM, Stanford MR. Endogenous bacterial endophthalmitis: a 17-year prospective series and review of 267 reported cases. Surv Ophthalmol. 2003;48(4):403–423. - PubMed
-
- Han DP, Wisniewski SR, Wilson LA, et al. Spectrum and susceptibilities of microbiologic isolates in the Endophthalmitis Vitrectomy Study. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996;122(1):1–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

