5-Fluorouracil-loaded poly(ε-caprolactone) nanoparticles combined with phage E gene therapy as a new strategy against colon cancer
- PMID: 22275826
- PMCID: PMC3260954
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S26401
5-Fluorouracil-loaded poly(ε-caprolactone) nanoparticles combined with phage E gene therapy as a new strategy against colon cancer
Abstract
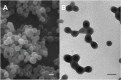
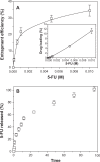
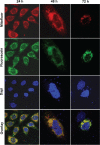
This work aimed to develop a new therapeutic approach to increase the efficacy of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in the treatment of advanced or recurrent colon cancer. 5-FU-loaded biodegradable poly(ε-caprolactone) nanoparticles (PCL NPs) were combined with the cytotoxic suicide gene E (combined therapy). The SW480 human cancer cell line was used to assay the combined therapeutic strategy. This cell line was established from a primary adenocarcinoma of the colon and is characterized by an intrinsically high resistance to apoptosis that correlates with its resistance to 5-FU. 5-FU was absorbed into the matrix of the PCL NPs during synthesis using the interfacial polymer disposition method. The antitumor activity of gene E from the phage ϕX174 was tested by generating a stable clone (SW480/12/E). In addition, the localization of E protein and its activity in mitochondria were analyzed. We found that the incorporation of 5-FU into PCL NPs (which show no cytotoxicity alone), significantly improved the drug's anticancer activity, reducing the proliferation rate of colon cancer cells by up to 40-fold when compared with the nonincorporated drug alone. Furthermore, E gene expression sensitized colon cancer cells to the cytotoxic action of the 5-FU-based nanomedicine. Our findings demonstrate that despite the inherent resistance of SW480 to apoptosis, E gene activity is mediated by an apoptotic phenomenon that includes modulation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 expression and intense mitochondrial damage. Finally, a strongly synergistic antiproliferative effect was observed in colon cancer cells when E gene expression was combined with the activity of the 5-FU-loaded PCL NPs, thereby indicating the potential therapeutic value of the combined therapy.
Keywords: 5-fluorouracil; E gene; colon cancer; combined therapy; gene therapy; poly (ε-caprolactone).
Figures





References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Berrino F, De Angelis R, Sant M, et al. Survival for eight major cancers and all cancers combined for European adults diagnosed in 1995–1999: results of the EUROCARE-4 study. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:773–783. - PubMed
-
- Bertolini A, Fiumano M, Muffatti A, et al. Acute cardiotoxicity from 5-fluorouracil: an underestimated toxicity. Minerva Cardioangiol. 1999;47:269–273. - PubMed
-
- Cooke JWB, Bright R, Coleman MJ, Jenkins KP. Process research and development of a dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase inactivator: Large-scale preparation of eniluracil using a Sonogashira coupling. Org Process Res Dev. 2001;5:383–336.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

