Reduced reward-related probability learning in schizophrenia patients
- PMID: 22275843
- PMCID: PMC3261650
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S26243
Reduced reward-related probability learning in schizophrenia patients
Abstract
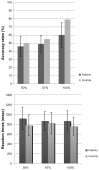
Although it is known that individuals with schizophrenia demonstrate marked impairment in reinforcement learning, the details of this impairment are not known. The aim of this study was to test the hypothesis that reward-related probability learning is altered in schizophrenia patients. Twenty-five clinically stable schizophrenia patients and 25 age- and gender-matched controls participated in the study. A simple gambling paradigm was used in which five different cues were associated with different reward probabilities (50%, 67%, and 100%). Participants were asked to make their best guess about the reward probability of each cue. Compared with controls, patients had significant impairment in learning contingencies on the basis of reward-related feedback. The correlation analyses revealed that the impairment of patients partially correlated with the severity of negative symptoms as measured on the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale but that it was not related to antipsychotic dose. In conclusion, the present study showed that the schizophrenia patients had impaired reward-based learning and that this was independent from their medication status.
Keywords: motivation; punishment; reinforcement learning; reward.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Altered activation in association with reward-related trial-and-error learning in patients with schizophrenia.Neuroimage. 2010 Mar;50(1):223-32. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.12.031. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Neuroimage. 2010. PMID: 20006717
-
An fMRI study of reward-related probability learning.Neuroimage. 2005 Feb 1;24(3):862-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.10.002. Epub 2004 Nov 18. Neuroimage. 2005. PMID: 15652321 Clinical Trial.
-
General functioning predicts reward and punishment learning in schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2011 Apr;127(1-3):131-6. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2010.07.028. Epub 2010 Aug 25. Schizophr Res. 2011. PMID: 20797838
-
Reward processing in schizophrenia: a deficit in the representation of value.Schizophr Bull. 2008 Sep;34(5):835-47. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbn068. Epub 2008 Jun 30. Schizophr Bull. 2008. PMID: 18591195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PSYCHOLOGICAL DEFICIT IN SCHIZOPHRENIA: I. AFFECT, REINFORCEMENT, AND CONCEPT ATTAINMENT.J Abnorm Psychol. 1965 Feb;70:2-24. doi: 10.1037/h0021685. J Abnorm Psychol. 1965. PMID: 14271288 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Reconceptualizing anhedonia: novel perspectives on balancing the pleasure networks in the human brain.Front Behav Neurosci. 2015 Mar 11;9:49. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00049. eCollection 2015. Front Behav Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25814941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The NEWMEDS rodent touchscreen test battery for cognition relevant to schizophrenia.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Nov;232(21-22):3853-72. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-4007-x. Epub 2015 Jul 24. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 26202612 Review.
-
Reinforcement learning and dopamine in schizophrenia: dimensions of symptoms or specific features of a disease group?Front Psychiatry. 2013 Dec 23;4:172. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00172. Front Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 24391603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probabilistic Reversal Learning in Schizophrenia: Stability of Deficits and Potential Causal Mechanisms.Schizophr Bull. 2016 Jul;42(4):942-51. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbv226. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Schizophr Bull. 2016. PMID: 26884546 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring anhedonia: impaired ability to pursue, experience, and learn about reward.Front Psychol. 2015 Sep 17;6:1409. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01409. eCollection 2015. Front Psychol. 2015. PMID: 26441781 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Breiter HC, Aharon I, Kahneman D, Dale A, Shizgal P. Functional imaging of neural responses to expectancy and experience of monetary gains and losses. Neuron. 2001;30(2):619–639. - PubMed
-
- Becerra L, Breiter HC, Wise R, Gonzalez RG, Borsook D. Reward circuitry activation by noxious thermal stimuli. Neuron. 2001;32(5):927–946. - PubMed
-
- Fareri DS, Martin LN, Delgado MR. Reward-related processing in the human brain: developmental considerations. Dev Psychopathol. 2008;20(4):1191–1211. - PubMed
-
- Houk JC, Wise SP. Distributed modular architectures linking basal ganglia, cerebellum, and cerebral cortex: their role in planning and controlling action. Cereb Cortex. 1995;5(2):95–110. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources