Impaired chromatin remodelling at STAT1-regulated promoters leads to global unresponsiveness of Toxoplasma gondii-infected macrophages to IFN-γ
- PMID: 22275866
- PMCID: PMC3262016
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002483
Impaired chromatin remodelling at STAT1-regulated promoters leads to global unresponsiveness of Toxoplasma gondii-infected macrophages to IFN-γ
Abstract
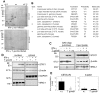
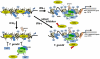
Intracellular pathogens including the apicomplexan and opportunistic parasite Toxoplasma gondii profoundly modify their host cells in order to establish infection. We have shown previously that intracellular T. gondii inhibit up-regulation of regulatory and effector functions in murine macrophages (MΦ) stimulated with interferon (IFN)-γ, which is the cytokine crucial for controlling the parasites' replication. Using genome-wide transcriptome analysis we show herein that infection with T. gondii leads to global unresponsiveness of murine macrophages to IFN-γ. More than 61% and 89% of the transcripts, which were induced or repressed by IFN-γ in non-infected MΦ, respectively, were not altered after stimulation of T. gondii-infected cells with IFN-γ. These genes are involved in a variety of biological processes, which are mostly but not exclusively related to immune responses. Analyses of the underlying mechanisms revealed that IFN-γ-triggered nuclear translocation of STAT1 still occurred in Toxoplasma-infected MΦ. However, STAT1 bound aberrantly to oligonucleotides containing the IFN-γ-responsive gamma-activated site (GAS) consensus sequence. Conversely, IFN-γ did not induce formation of active GAS-STAT1 complexes in nuclear extracts from infected MΦ. Mass spectrometry of protein complexes bound to GAS oligonucleotides showed that T. gondii-infected MΦ are unable to recruit non-muscle actin to IFN-γ-responsive DNA sequences, which appeared to be independent of stimulation with IFN-γ and of STAT1 binding. IFN-γ-induced recruitment of BRG-1 and acetylation of core histones at the IFN-γ-regulated CIITA promoter IV, but not β-actin was diminished by >90% in Toxoplasma-infected MΦ as compared to non-infected control cells. Remarkably, treatment with histone deacetylase inhibitors restored the ability of infected macrophages to express the IFN-γ regulated genes H2-A/E and CIITA. Taken together, these results indicate that Toxoplasma-infected MΦ are unable to respond to IFN-γ due to disturbed chromatin remodelling, but can be rescued using histone deacetylase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




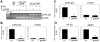

Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 augments expression of a subset of IFN-γ-regulated genes in Toxoplasma gondii-infected macrophages but does not improve parasite control.Exp Parasitol. 2017 Sep;180:45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2017.02.011. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Exp Parasitol. 2017. PMID: 28189488
-
Epigenetic Control of IFN-γ Host Responses During Infection With Toxoplasma gondii.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 25;11:581241. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.581241. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33072127 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii stabilises tetrameric complexes of tyrosine-phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 and leads to its sustained and promiscuous DNA binding.Cell Microbiol. 2018 Nov;20(11):e12887. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12887. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Cell Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29968354
-
From cells to signaling cascades: manipulation of innate immunity by Toxoplasma gondii.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003 Dec 5;39(3):193-203. doi: 10.1016/S0928-8244(03)00279-7. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14642303 Review.
-
IFNs in host defence and parasite immune evasion during Toxoplasma gondii infections.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 7;15:1356216. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1356216. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38384452 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An in silico pipeline to filter the Toxoplasma gondii proteome for proteins that could traffic to the host cell nucleus and influence host cell epigenetic regulation.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2018;113(6):e170471. doi: 10.1590/0074-02760170471. Epub 2018 May 28. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2018. PMID: 29846382 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent co-transcriptomes of different host cells infected with Toxoplasma gondii reveal cell type-specific host-parasite interactions.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 3;7(1):7229. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07838-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28775382 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii clonal strains all inhibit STAT1 transcriptional activity but polymorphic effectors differentially modulate IFNγ induced gene expression and STAT1 phosphorylation.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51448. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051448. Epub 2012 Dec 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23240025 Free PMC article.
-
The enemy within: Targeting host-parasite interaction for antileishmanial drug discovery.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017 Jun 8;11(6):e0005480. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005480. eCollection 2017 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017. PMID: 28594938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics of host-pathogen interactions: the road ahead and the road behind.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(11):e1003007. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003007. Epub 2012 Nov 29. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23209403 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Montoya JG, Liesenfeld O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet. 2004;363:1965–1976. - PubMed
-
- Lüder CG, Stanway RR, Chaussepied M, Langsley G, Heussler VT. Intracellular survival of apicomplexan parasites and host cell modification. Int J Parasitol. 2009;39:163–173. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki Y, Orellana MA, Schreiber RD, Remington JS. Interferon-gamma: the major mediator of resistance against Toxoplasma gondii. Science. 1988;240:516–518. - PubMed
-
- Gazzinelli RT, Hakim FT, Hieny S, Shearer GM, Sher A. Synergistic role of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes in IFN-gamma production and protective immunity induced by an attenuated Toxoplasma gondii vaccine. J Immunol. 1991;146:286–292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

