Analysis of Synaptotagmin, SV2, and Rab3 Expression in Cortical Glutamatergic and GABAergic Axon Terminals
- PMID: 22275882
- PMCID: PMC3254050
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2011.00032
Analysis of Synaptotagmin, SV2, and Rab3 Expression in Cortical Glutamatergic and GABAergic Axon Terminals
Abstract
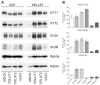
We investigated whether cortical glutamatergic and GABAergic release machineries can be differentiated on the basis of the nature and amount of proteins they express, by performing a quantitative analysis of the degree of co-localization of synaptotagmin (SYT) 1 and 2, synaptic vesicle protein 2 (SV2) A and B, and Rab3a and c in VGLUT1+, VGLUT2+, and VGAT+ terminals and synaptic vesicles (SVs) in rat cerebral cortex. Co-localization studies showed that VGLUT1 puncta had high levels of SV2A and B and of Rab3c, intermediate levels of SYT1, and low levels of SYT2 and Rab3c; VGLUT2 puncta exhibited intermediate levels of all presynaptic proteins studied; whereas vesicular GABA transporter (VGAT) puncta had high levels of SV2A and SYT2, intermediate levels of SYT1, Rab3a, and Rab3c, and low levels of SV2B. Since SV2B is reportedly expressed by glutamatergic neurons and we observed SV2B expression in VGAT puncta, we performed electron microscopic studies and found SV2B positive axon terminals forming symmetric synapses. Immunoisolation studies showed that the expression levels of the protein isoforms varied in the three populations of SVs. Expression of SYT1 was highest in VGLUT1-SVs, while SYT2 expression was similar in the three SV groups. Expression of SV2A was similarly high in all three SV populations, except for SV2B levels that were very low in VGAT SVs. Finally, Rab3a levels were similar in the three SV groups, while Rab3c levels were highest in VGLUT1-SVs. These quantitative results extend our previous studies on the differential expression of presynaptic proteins involved in neurotransmitter release in GABAergic and glutamatergic terminals and indicate that heterogeneity of the respective release machineries can be generated by the differential complement of SV proteins involved in distinct stages of the release process.
Keywords: Rab3; SV2; VGAT; VGLUT1; VGLUT2; synaptotagmin.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Heterogeneity of glutamatergic and GABAergic release machinery in cerebral cortex: analysis of synaptogyrin, vesicle-associated membrane protein, and syntaxin.Neuroscience. 2010 Feb 3;165(3):934-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.11.009. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 19909789
-
Heterogeneity of glutamatergic and GABAergic release machinery in cerebral cortex.Neuroscience. 2007 Jun 8;146(4):1829-40. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.02.060. Epub 2007 Apr 19. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17445987
-
VGLUT1 and VGAT are sorted to the same population of synaptic vesicles in subsets of cortical axon terminals.J Neurochem. 2009 Sep;110(5):1538-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06251.x. Epub 2009 Jul 15. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19627441
-
Expression of Neurofilament Subunits at Neocortical Glutamatergic and GABAergic Synapses.Front Neuroanat. 2018 Sep 11;12:74. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2018.00074. eCollection 2018. Front Neuroanat. 2018. PMID: 30254572 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity of axon terminals expressing VGLUT1 in the cerebral neocortex.Arch Ital Biol. 2005 May;143(2):127-32. Arch Ital Biol. 2005. PMID: 16106993 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression profile of synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2A, B, and C paralogues in temporal neocortex tissue from patients with temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE).Mol Brain. 2022 May 16;15(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13041-022-00931-w. Mol Brain. 2022. PMID: 35578248 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Fluorescent Small Molecule Compounds for Synaptic Labeling by Image-Based, High-Content Screening.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018 Apr 18;9(4):673-683. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00263. Epub 2017 Dec 18. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29215865 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of metabotropic glutamate and GABA receptors at neocortical glutamatergic and GABAergic axon terminals.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Sep 4;9:345. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00345. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26388733 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of oligodendrocyte ErbB receptor signaling leads to hypomyelination, reduced density of parvalbumin-expressing interneurons, and inhibitory function in the auditory cortex.Glia. 2023 Feb;71(2):187-204. doi: 10.1002/glia.24266. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Glia. 2023. PMID: 36052476 Free PMC article.
-
Efferent innervation of turtle semicircular canal cristae: comparisons with bird and mouse.J Comp Neurol. 2015 Jun 1;523(8):1258-80. doi: 10.1002/cne.23738. Epub 2015 Mar 25. J Comp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25560461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso-Nanclares L., Minelli A., Melone M., Edwards R. H., Defelipe J., Conti F. (2004). Perisomatic glutamatergic axon terminals: a novel feature of cortical synaptology revealed by vesicular glutamate transporter 1 immunostaining. Neuroscience 123, 547–55610.1016/j.neuroscience.2003.09.033 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

