Multiscale exploration of mouse brain microstructures using the knife-edge scanning microscope brain atlas
- PMID: 22275895
- PMCID: PMC3254184
- DOI: 10.3389/fninf.2011.00029
Multiscale exploration of mouse brain microstructures using the knife-edge scanning microscope brain atlas
Abstract
Connectomics is the study of the full connection matrix of the brain. Recent advances in high-throughput, high-resolution 3D microscopy methods have enabled the imaging of whole small animal brains at a sub-micrometer resolution, potentially opening the road to full-blown connectomics research. One of the first such instruments to achieve whole-brain-scale imaging at sub-micrometer resolution is the Knife-Edge Scanning Microscope (KESM). KESM whole-brain data sets now include Golgi (neuronal circuits), Nissl (soma distribution), and India ink (vascular networks). KESM data can contribute greatly to connectomics research, since they fill the gap between lower resolution, large volume imaging methods (such as diffusion MRI) and higher resolution, small volume methods (e.g., serial sectioning electron microscopy). Furthermore, KESM data are by their nature multiscale, ranging from the subcellular to the whole organ scale. Due to this, visualization alone is a huge challenge, before we even start worrying about quantitative connectivity analysis. To solve this issue, we developed a web-based neuroinformatics framework for efficient visualization and analysis of the multiscale KESM data sets. In this paper, we will first provide an overview of KESM, then discuss in detail the KESM data sets and the web-based neuroinformatics framework, which is called the KESM brain atlas (KESMBA). Finally, we will discuss the relevance of the KESMBA to connectomics research, and identify challenges and future directions.
Keywords: Golgi; Knife-Edge Scanning Microscopy; connectomics; mouse brain; multiscale; web-based brain atlas.
Figures
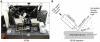


Similar articles
-
Specimen preparation, imaging, and analysis protocols for knife-edge scanning microscopy.J Vis Exp. 2011 Dec 9;(58):3248. doi: 10.3791/3248. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 22215068 Free PMC article.
-
Tracing and analysis of the whole mouse brain vasculature with systematic cleaning to remove and consolidate erroneous images.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018 Jul;2018:143-146. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2018.8512215. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018. PMID: 30440359
-
Fast submicrometer-scale imaging of whole zebrafish using the knife-edge scanning microscope.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2016 Aug;2016:5901-5904. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2016.7592071. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2016. PMID: 28269597
-
Mission (im)possible - mapping the brain becomes a reality.Microscopy (Oxf). 2015 Feb;64(1):45-55. doi: 10.1093/jmicro/dfu104. Epub 2014 Dec 26. Microscopy (Oxf). 2015. PMID: 25542963 Review.
-
Connectomics: comprehensive approaches for whole-brain mapping.Microscopy (Oxf). 2015 Feb;64(1):57-67. doi: 10.1093/jmicro/dfu103. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Microscopy (Oxf). 2015. PMID: 25527636 Review.
Cited by
-
Staining and embedding the whole mouse brain for electron microscopy.Nat Methods. 2012 Dec;9(12):1198-201. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2213. Epub 2012 Oct 21. Nat Methods. 2012. PMID: 23085613
-
Mapping the connectome: multi-level analysis of brain connectivity.Front Neuroinform. 2012 May 1;6:14. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2012.00014. eCollection 2012. Front Neuroinform. 2012. PMID: 22557964 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Accurate flow in augmented networks (AFAN): an approach to generating three-dimensional biomimetic microfluidic networks with controlled flow.Anal Methods. 2019 Jan 7;11(1):8-16. doi: 10.1039/c8ay01798k. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Anal Methods. 2019. PMID: 31490456 Free PMC article.
-
Precise Cerebral Vascular Atlas in Stereotaxic Coordinates of Whole Mouse Brain.Front Neuroanat. 2017 Dec 19;11:128. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2017.00128. eCollection 2017. Front Neuroanat. 2017. PMID: 29311856 Free PMC article.
-
Image-guided, Laser-based Fabrication of Vascular-derived Microfluidic Networks.J Vis Exp. 2017 Jan 3;(119):55101. doi: 10.3791/55101. J Vis Exp. 2017. PMID: 28117805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott L. C. (2008). “High-throughput imaging of whole small animal brains with the knife-edge scanning microscope,” in Neuroscience Meeting Planner, Program No. 504.2. Washington, DC: Society for Neuroscience
-
- Ascoli G. A., Donohue D. E., Halavi M. (2007). NeuroMorpho.Org: a central resource for neuronal morphologies. J. Neurosci. 27, 9247–925110.1523/JNEUROSCI.2055-07.2007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

