COINS: An Innovative Informatics and Neuroimaging Tool Suite Built for Large Heterogeneous Datasets
- PMID: 22275896
- PMCID: PMC3250631
- DOI: 10.3389/fninf.2011.00033
COINS: An Innovative Informatics and Neuroimaging Tool Suite Built for Large Heterogeneous Datasets
Abstract
The availability of well-characterized neuroimaging data with large numbers of subjects, especially for clinical populations, is critical to advancing our understanding of the healthy and diseased brain. Such data enables questions to be answered in a much more generalizable manner and also has the potential to yield solutions derived from novel methods that were conceived after the original studies' implementation. Though there is currently growing interest in data sharing, the neuroimaging community has been struggling for years with how to best encourage sharing data across brain imaging studies. With the advent of studies that are much more consistent across sites (e.g., resting functional magnetic resonance imaging, diffusion tensor imaging, and structural imaging) the potential of pooling data across studies continues to gain momentum. At the mind research network, we have developed the collaborative informatics and neuroimaging suite (COINS; http://coins.mrn.org) to provide researchers with an information system based on an open-source model that includes web-based tools to manage studies, subjects, imaging, clinical data, and other assessments. The system currently hosts data from nine institutions, over 300 studies, over 14,000 subjects, and over 19,000 MRI, MEG, and EEG scan sessions in addition to more than 180,000 clinical assessments. In this paper we provide a description of COINS with comparison to a valuable and popular system known as XNAT. Although there are many similarities between COINS and other electronic data management systems, the differences that may concern researchers in the context of multi-site, multi-organizational data sharing environments with intuitive ease of use and PHI security are emphasized as important attributes.
Keywords: brain imaging; database; neuroinformatics.
Figures
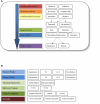

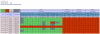

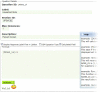

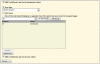
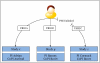



Similar articles
-
Automated collection of imaging and phenotypic data to centralized and distributed data repositories.Front Neuroinform. 2014 Jun 5;8:60. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2014.00060. eCollection 2014. Front Neuroinform. 2014. PMID: 24926252 Free PMC article.
-
COINS Data Exchange: An open platform for compiling, curating, and disseminating neuroimaging data.Neuroimage. 2016 Jan 1;124(Pt B):1084-1088. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.05.049. Epub 2015 May 24. Neuroimage. 2016. PMID: 26019122 Free PMC article.
-
The Developmental Chronnecto-Genomics (Dev-CoG) study: A multimodal study on the developing brain.Neuroimage. 2021 Jan 15;225:117438. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117438. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 33039623 Free PMC article.
-
Federated Analysis of Neuroimaging Data: A Review of the Field.Neuroinformatics. 2022 Apr;20(2):377-390. doi: 10.1007/s12021-021-09550-7. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Neuroinformatics. 2022. PMID: 34807353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroinformatics Software Applications Supporting Electronic Data Capture, Management, and Sharing for the Neuroimaging Community.Neuropsychol Rev. 2015 Sep;25(3):356-68. doi: 10.1007/s11065-015-9293-x. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Neuropsychol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26267019 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Scan Once, Analyse Many: Using Large Open-Access Neuroimaging Datasets to Understand the Brain.Neuroinformatics. 2022 Jan;20(1):109-137. doi: 10.1007/s12021-021-09519-6. Epub 2021 May 11. Neuroinformatics. 2022. PMID: 33974213 Free PMC article.
-
Sharing data in the global alzheimer's association interactive network.Neuroimage. 2016 Jan 1;124(Pt B):1168-1174. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.05.082. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Neuroimage. 2016. PMID: 26049147 Free PMC article.
-
COINSTAC: A Privacy Enabled Model and Prototype for Leveraging and Processing Decentralized Brain Imaging Data.Front Neurosci. 2016 Aug 19;10:365. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00365. eCollection 2016. Front Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27594820 Free PMC article.
-
Independent vector analysis for common subspace analysis: Application to multi-subject fMRI data yields meaningful subgroups of schizophrenia.Neuroimage. 2020 Aug 1;216:116872. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116872. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 32353485 Free PMC article.
-
MIRMAID: A Content Management System for Medical Image Analysis Research.Radiographics. 2015 Sep-Oct;35(5):1461-8. doi: 10.1148/rg.2015140031. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Radiographics. 2015. PMID: 26284301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen E., Erhardt E., Damaraju E., Gruner W., Segall J., Silva R., Havlicek M., Rachakonda S., Fries J., Kalyanam R., Michael A., Turner J., Eichele T., Adelsheim S., Bryan A., Bustillo J. R., Clark V. P., Feldstein S., Filbey F. M., Ford C., Hutchison K., Jung R., Kiehl K. A., Kodituwakku P., Komesu Y., Mayer A. R., Pearlson G. D., Phillips J., Sadek J., Stevens M., Teuscher U., Thoma R. J., Calhoun V. D. (2011). A baseline for the multivariate comparison of resting state networks. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 5:2.10.3389/fnsys.2011.00002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bockholt H. J., Scully M., Courtney W., Rachakonda S., Scott A., Caprihan A., Fries J., Kalyanam R., Segall J., De la Garza R., Lane S., Calhoun V. D. (2010). Mining the mind research network: a novel framework for exploring large scale, heterogeneous translational neuroscience research data sources. Front. Neuroinform. 3:36.10.3389/neuro.11.036.2009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buccigrossi R., Ellisman M., Grethe J., Haselgrove C., Kennedy D. N., Martone M., Preuss N., Reynolds K., Sullivan M., Turner J., Wagner K. (2008). The neuroimaging informatics tools and resources clearinghouse (NITRC). AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2008, 1000. - PubMed
-
- Dinov I., Lozev K., Petrosyan P., Liu Z., Eggert P., Pierce J., Zamanyan A., Chakrapani S., Van Horn J., Parker D. S., Magsipoc R., Leung K., Gutman B., Woods R., Toga A. (2010). Neuroimaging study designs, computational analyses and data provenance using the LONI pipeline. PLoS ONE 5, e13070.10.1371/journal.pone.0013070 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- First M. B., Spitzer R. L., Gibbon M., Williams J. B. W. (1995). Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV axis I Disorders-Patient Edition (SCID-I/P, Version 2.0). New York: Biometrics Research Department, New York State Psychiatric Institute
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

