IART (Intra-Operative Avidination for Radionuclide Therapy) for accelerated radiotherapy in breast cancer patients. Technical aspects and preliminary results of a phase II study with 90Y-labelled biotin
- PMID: 22276027
- PMCID: PMC3234029
- DOI: 10.3332/ecancer.2010.166
IART (Intra-Operative Avidination for Radionuclide Therapy) for accelerated radiotherapy in breast cancer patients. Technical aspects and preliminary results of a phase II study with 90Y-labelled biotin
Abstract
Background: Breast conserving surgery (BCS) plus external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) is considered the standard treatment for early breast cancer. We have investigated the possibility of irradiating the residual gland, using an innovative nuclear medicine approach named IART(®) (Intra-operative Avidination for Radionuclide Therapy).
Aim: The objective of this study was to determine the optimal dose of avidin with a fixed activity (3.7 GBq) of (90)Y-biotin, in order to provide a boost of 20 Gy, followed by EBRT to the whole breast (WB) at the reduced dose of 40 Gy. Local and systemic toxicity, patient's quality of life, including the cosmetic results after the combined treatment with IART(®) and EBRT, were assessed.
Methods: After tumour excision, the surgeon injected native avidin diluted in 30 ml of saline solution into and around the tumour bed (see video). Patients received one of three avidin dose levels: 50 mg (10 pts), 100 mg (15 pts) and 150 mg (10 pts). Between 12 to 24 h after surgery, 3.7 GBq (90)Y-biotin spiked with 185 MBq (111)In-biotin was administered intravenously (i.v.). Whole body scans and SPECT images were performed up to 30 h post-injection for dosimetric purposes. WB-EBRT was administered four weeks after the IART(®) boost. Local toxicity and quality of life were evaluated.
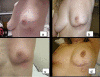
Results: Thirty-five patients were evaluated. No side effects were observed after avidin administration and (90)Y-biotin infusion. An avidin dose level of 100 mg resulted the most appropriate in order to deliver the required radiation dose (19.5 ± 4.0 Gy) to the surgical bed. At the end of IART(®), no local toxicity occurred and the overall cosmetic result was good. The tolerance to the reduced EBRT was also good. The highest grade of transient local toxicity was G3, which occurred in 3/32 pts following the completion of WB-EBRT. The combination of IART(®)+EBRT was well accepted by the patients, without any changes to their quality of life.
Conclusions: These preliminary results support the hypothesis that IART(®) may represent a valid approach to accelerated WB irradiation after BCS. We hope that this nuclear medicine technique will contribute to a better management of breast cancer patients.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Intraoperative avidination for radionuclide treatment as a radiotherapy boost in breast cancer: results of a phase II study with (90)Y-labeled biotin.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010 Feb;37(2):203-11. doi: 10.1007/s00259-009-1260-4. Epub 2009 Sep 4. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010. PMID: 19760414 Clinical Trial.
-
3D dosimetry in patients with early breast cancer undergoing Intraoperative Avidination for Radionuclide Therapy (IART) combined with external beam radiation therapy.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012 Nov;39(11):1702-11. doi: 10.1007/s00259-012-2197-6. Epub 2012 Aug 14. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22890802
-
IART: intraoperative avidination for radionuclide treatment. A new way of partial breast irradiation.Breast. 2007 Feb;16(1):17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2006.10.003. Epub 2006 Dec 14. Breast. 2007. PMID: 17174093
-
Breast-conserving surgery with intra-operative radiotherapy: the right approach for the 21st century?Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2006 Apr;18(3):220-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2005.11.017. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2006. PMID: 16605053 Review.
-
Radiotherapy confined to the tumor bed following breast conserving surgery current status, controversies, and future projects.Strahlenther Onkol. 2002 Nov;178(11):597-606. doi: 10.1007/s00066-002-0966-z. Strahlenther Onkol. 2002. PMID: 12426670 Review.
Cited by
-
Radiometals in Imaging and Therapy: Highlighting Two Decades of Research.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 13;16(10):1460. doi: 10.3390/ph16101460. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intraoperative radiotherapy in early stage breast cancer: potential indications and evidence to date.Br J Radiol. 2015 May;88(1049):20140686. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140686. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Br J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25734489 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Levitt SH, Aeppli DM, Nierengarten ME. The impact of radiation on early breast carcinoma. Cancer. 1996;75:1035–42. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
