Absolute oxygenation metabolism measurements using magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 22276084
- PMCID: PMC3256581
- DOI: 10.2174/1874440001105010120
Absolute oxygenation metabolism measurements using magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
Cerebral oxygen metabolism plays a critical role in maintaining normal function of the brain. It is the primary energy source to sustain neuronal functions. Abnormalities in oxygen metabolism occur in various neuro-pathologic conditions such as ischemic stroke, cerebral trauma, cancer, Alzheimer's disease and shock. Therefore, the ability to quantitatively measure tissue oxygenation and oxygen metabolism is essential to the understanding of pathophysiology and treatment of various diseases. The focus of this review is to provide an introduction of various blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) contrast methods for absolute measurements of tissue oxygenation, including both magnitude and phase image based approaches. The advantages and disadvantages of each method are discussed.
Keywords: Magnetic resonance imaging; blood oxygenation level dependent; cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen utilization; cerebral oxygen saturation; oxygen extraction fraction; oxygenation metabolism quantification; susceptibility weighted imaging..
Figures

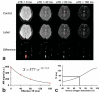
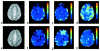
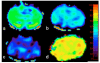
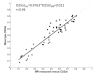

Similar articles
-
Blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD)-based techniques for the quantification of brain hemodynamic and metabolic properties - theoretical models and experimental approaches.NMR Biomed. 2013 Aug;26(8):963-86. doi: 10.1002/nbm.2839. Epub 2012 Aug 28. NMR Biomed. 2013. PMID: 22927123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxygen metabolism in ischemic stroke using magnetic resonance imaging.Transl Stroke Res. 2012 Mar;3(1):65-75. doi: 10.1007/s12975-011-0141-x. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Transl Stroke Res. 2012. PMID: 24323755
-
Imaging Oxygen Metabolism In Acute Stroke Using MRI.Curr Radiol Rep. 2014 Mar 1;2(3):39. doi: 10.1007/s40134-013-0039-3. Curr Radiol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24707451 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of Cerebral Oxygen Extraction Fraction Using Quantitative BOLD Approach: A Review.Phenomics. 2022 Dec 5;3(1):101-118. doi: 10.1007/s43657-022-00081-y. eCollection 2023 Feb. Phenomics. 2022. PMID: 36939794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative functional imaging of the brain: towards mapping neuronal activity by BOLD fMRI.NMR Biomed. 2001 Nov-Dec;14(7-8):413-31. doi: 10.1002/nbm.733. NMR Biomed. 2001. PMID: 11746934
Cited by
-
Computational Model for Tumor Oxygenation Applied to Clinical Data on Breast Tumor Hemoglobin Concentrations Suggests Vascular Dilatation and Compression.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 22;11(8):e0161267. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161267. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27547939 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen metabolism in acute ischemic stroke.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018 Sep;38(9):1481-1499. doi: 10.1177/0271678X17722095. Epub 2017 Aug 9. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018. PMID: 28792276 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grotta JC. Emerging stroke therapies. Semin Neurol. 1986;6(3 ):285–92. - PubMed
-
- Heiss WD, Graf R, Wienhard K, et al. Dynamic penumbra demonstrated by sequential multitracer PET after middle cerebral artery occlusion in cats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1994;14(6 ):892–902. - PubMed
-
- Baron JC, Rougemont D, Soussaline F, et al. Local interrelationships of cerebral oxygen consumption and glucose utilization in normal subjects and in ischemic stroke patients: a positron tomography study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1984;4(2 ):140–9. - PubMed
-
- Powers WJ, Grubb RL, Darriet D, Raichle ME. Cerebral blood flow and cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen requirements for cerebral function and viability in humans. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1985;5(4 ):600–8. - PubMed
-
- Marchal G, Benali K, Iglesias S, Viader F, Derlon JM, Baron JC. Voxel-based mapping of irreversible ischaemic damage with PET in acute stroke. Brain. 1999;122 ( Pt 12 ):2387–400. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
