A novel, "double-clamp" binding mode for human heme oxygenase-1 inhibition
- PMID: 22276118
- PMCID: PMC3261875
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029514
A novel, "double-clamp" binding mode for human heme oxygenase-1 inhibition
Abstract
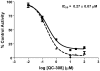
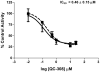
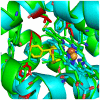
The development of heme oxygenase (HO) inhibitors is critical in dissecting and understanding the HO system and for potential therapeutic applications. We have established a program to design and optimize HO inhibitors using structure-activity relationships in conjunction with X-ray crystallographic analyses. One of our previous complex crystal structures revealed a putative secondary hydrophobic binding pocket which could be exploited for a new design strategy by introducing a functional group that would fit into this potential site. To test this hypothesis and gain further insights into the structural basis of inhibitor binding, we have synthesized and characterized 1-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-4,4-diphenyl-2-butanone (QC-308). Using a carbon monoxide (CO) formation assay on rat spleen microsomes, the compound was found to be ∼15 times more potent (IC(50) = 0.27±0.07 µM) than its monophenyl analogue, which is already a potent compound in its own right (QC-65; IC(50) = 4.0±1.8 µM). The crystal structure of hHO-1 with QC-308 revealed that the second phenyl group in the western region of the compound is indeed accommodated by a definitive secondary proximal hydrophobic pocket. Thus, the two phenyl moieties are each stabilized by distinct hydrophobic pockets. This "double-clamp" binding offers additional inhibitor stabilization and provides a new route for improvement of human heme oxygenase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




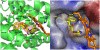

Similar articles
-
X-ray crystal structure of human heme oxygenase-1 with (2R,4S)-2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]-2-[(1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]-4[((5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yl)thio)methyl]-1,3-dioxolane: a novel, inducible binding mode.J Med Chem. 2009 Aug 13;52(15):4946-50. doi: 10.1021/jm900434f. J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19601578
-
X-ray crystal structure of human heme oxygenase-1 in complex with 1-(adamantan-1-yl)-2-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethanone: a common binding mode for imidazole-based heme oxygenase-1 inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2008 Oct 9;51(19):5943-52. doi: 10.1021/jm800505m. Epub 2008 Sep 18. J Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18798608
-
Structural characterization of human heme oxygenase-1 in complex with azole-based inhibitors.J Inorg Biochem. 2010 Mar;104(3):324-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2009.10.011. Epub 2009 Oct 24. J Inorg Biochem. 2010. PMID: 19917515 Review.
-
Heme oxygenase inhibition by 2-oxy-substituted 1-azolyl-4-phenylbutanes: effect of variation of the azole moiety. X-ray crystal structure of human heme oxygenase-1 in complex with 4-phenyl-1-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-2-butanone.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2010 Jan;75(1):68-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2009.00909.x. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2010. PMID: 19954435
-
Structural Insights into Azole-based Inhibitors of Heme Oxygenase-1: Development of Selective Compounds for Therapeutic Applications.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(42):5803-5821. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180606082512. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30674243 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthetically Lethal Interactions of Heme Oxygenase-1 and Fumarate Hydratase Genes.Biomolecules. 2020 Jan 16;10(1):143. doi: 10.3390/biom10010143. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 31963199 Free PMC article.
-
Senolysis induced by 25-hydroxycholesterol targets CRYAB in multiple cell types.iScience. 2022 Feb 2;25(2):103848. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103848. eCollection 2022 Feb 18. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35198901 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Novel Acetamide-Based Heme Oxygenase-1 Inhibitors with Potent In Vitro Antiproliferative Activity.J Med Chem. 2021 Sep 23;64(18):13373-13393. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00633. Epub 2021 Sep 2. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34472337 Free PMC article.
-
Heme-Dependent ER Stress Apoptosis: A Mechanism for the Selective Toxicity of the Dihydroartemisinin, NSC735847, in Colorectal Cancer Cells.Front Oncol. 2020 Jun 17;10:965. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00965. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32626657 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into human heme oxygenase-1 inhibition by potent and selective azole-based compounds.J R Soc Interface. 2013 Jan 6;10(78):20120697. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2012.0697. Epub 2012 Nov 8. J R Soc Interface. 2013. PMID: 23097500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tenhunen R, Marver HS, Schmid R. Microsomal heme oxygenase. Characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1969;244:6388–6394. - PubMed
-
- Vreman HJ, Wong RJ, Stevenson DK. Carbon Monoxide and Cardiovascular Function. Boca Raton, London, New York, Washington: CRC Press; 2002.
-
- Maines MD. The heme oxygenase system: a regulator of second messenger gases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1997;37:517–554. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi S, Omata Y, Sakamoto H, Higashimoto Y, Hara T, et al. Characterization of rat heme oxygenase-3 gene. Implication of processed pseudogenes derived from heme oxygenase-2 gene. Gene. 2004;336:241–250. - PubMed
-
- Ryter SW, Alam J, Choi AM. Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide: from basic science to therapeutic applications. Physiol Rev. 2006;86:583–650. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

