Analysis of marker-defined HNSCC subpopulations reveals a dynamic regulation of tumor initiating properties
- PMID: 22276135
- PMCID: PMC3262798
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029974
Analysis of marker-defined HNSCC subpopulations reveals a dynamic regulation of tumor initiating properties
Abstract
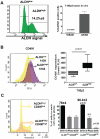
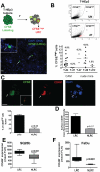
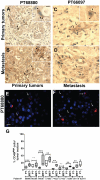
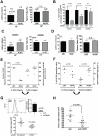
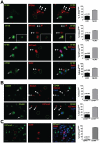
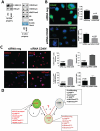
Head and neck squamous carcinoma (HNSCC) tumors carry dismal long-term prognosis and the role of tumor initiating cells (TICs) in this cancer is unclear. We investigated in HNSCC xenografts whether specific tumor subpopulations contributed to tumor growth. We used a CFSE-based label retentions assay, CD49f (α6-integrin) surface levels and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) activity to profile HNSCC subpopulations. The tumorigenic potential of marker-positive and -negative subpopulations was tested in nude (Balb/c nu/nu) and NSG (NOD.Cg-Prkdc(scid) Il2rg(tm1Wjl)/SzJ) mice and chicken embryo chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assays. Here we identified in HEp3, SQ20b and FaDu HNSCC xenografts a subpopulation of G0/G1-arrested slow-cycling CD49f(high)/ALDH1A1(high)/H3K4/K27me3(low) subpopulation (CD49f+) of tumor cells. A strikingly similar CD49f(high)/H3K27me3(low) subpopulation is also present in primary human HNSCC tumors and metastases. While only sorted CD49f(high)/ALDH(high), label retaining cells (LRC) proliferated immediately in vivo, with time the CD49f(low)/ALDH(low), non-LRC (NLRC) tumor cell subpopulations were also able to regain tumorigenic capacity; this was linked to restoration of CD49f(high)/ALDH(high), label retaining cells. In addition, CD49f is required for HEp3 cell tumorigenicity and to maintain low levels of H3K4/K27me3. CD49f+ cells also displayed reduced expression of the histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. This suggests that although transiently quiescent, their unique chromatin structure is poised for rapid transcriptional activation. CD49f- cells can "reprogram" and also achieve this state eventually. We propose that in HNSCC tumors, epigenetic mechanisms likely driven by CD49f signaling dynamically regulate HNSCC xenograft phenotypic heterogeneity. This allows multiple tumor cell subpopulations to drive tumor growth suggesting that their dynamic nature renders them a "moving target" and their eradication might require more persistent strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA expression profiles of cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Oncol. 2015 Oct;47(4):1249-56. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3145. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26323893 Free PMC article.
-
Single-marker identification of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cancer stem cells with aldehyde dehydrogenase.Head Neck. 2010 Sep;32(9):1195-201. doi: 10.1002/hed.21315. Head Neck. 2010. PMID: 20073073 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer stem cell related markers of radioresistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 27;6(33):34494-509. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5417. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26460734 Free PMC article.
-
C-Met pathway promotes self-renewal and tumorigenecity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma stem-like cell.Oral Oncol. 2014 Jul;50(7):633-9. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2014.04.004. Epub 2014 May 15. Oral Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24835851 Review.
-
Activation of Matrix Hyaluronan-Mediated CD44 Signaling, Epigenetic Regulation and Chemoresistance in Head and Neck Cancer Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Aug 24;18(9):1849. doi: 10.3390/ijms18091849. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28837080 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TGF-β-Induced Quiescence Mediates Chemoresistance of Tumor-Propagating Cells in Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cell Stem Cell. 2017 Nov 2;21(5):650-664.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2017.10.001. Cell Stem Cell. 2017. PMID: 29100014 Free PMC article.
-
Melanoma stem cells and metastasis: mimicking hematopoietic cell trafficking?Lab Invest. 2014 Jan;94(1):13-30. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2013.116. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Lab Invest. 2014. PMID: 24126889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inactivation of the mTORC1-eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E pathway alters stress granule formation.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jun;33(11):2285-301. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01517-12. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23547259 Free PMC article.
-
From single cells to deep phenotypes in cancer.Nat Biotechnol. 2012 Jul 10;30(7):639-47. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2283. Nat Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22781693 Review.
-
NR2F1 controls tumour cell dormancy via SOX9- and RARβ-driven quiescence programmes.Nat Commun. 2015 Jan 30;6:6170. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7170. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25636082 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

