Decreased autocrine EGFR signaling in metastatic breast cancer cells inhibits tumor growth in bone and mammary fat pad
- PMID: 22276166
- PMCID: PMC3261896
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030255
Decreased autocrine EGFR signaling in metastatic breast cancer cells inhibits tumor growth in bone and mammary fat pad
Abstract
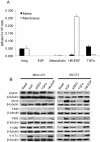
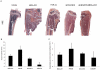
Breast cancer metastasis to bone triggers a vicious cycle of tumor growth linked to osteolysis. Breast cancer cells and osteoblasts express the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and produce ErbB family ligands, suggesting participation of these growth factors in autocrine and paracrine signaling within the bone microenvironment. EGFR ligand expression was profiled in the bone metastatic MDA-MB-231 cells (MDA-231), and agonist-induced signaling was examined in both breast cancer and osteoblast-like cells. Both paracrine and autocrine EGFR signaling were inhibited with a neutralizing amphiregulin antibody, PAR34, whereas shRNA to the EGFR was used to specifically block autocrine signaling in MDA-231 cells. The impact of these was evaluated with proliferation, migration and gene expression assays. Breast cancer metastasis to bone was modeled in female athymic nude mice with intratibial inoculation of MDA-231 cells, and cancer cell-bone marrow co-cultures. EGFR knockdown, but not PAR34 treatment, decreased osteoclasts formed in vitro (p<0.01), reduced osteolytic lesion tumor volume (p<0.01), increased survivorship in vivo (p<0.001), and resulted in decreased MDA-231 growth in the fat pad (p<0.01). Fat pad shEGFR-MDA-231 tumors produced in nude mice had increased necrotic areas and decreased CD31-positive vasculature. shEGFR-MDA-231 cells also produced decreased levels of the proangiogenic molecules macrophage colony stimulating factor-1 (MCSF-1) and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9), both of which were decreased by EGFR inhibitors in a panel of EGFR-positive breast cancer cells. Thus, inhibiting autocrine EGFR signaling in breast cancer cells may provide a means for reducing paracrine factor production that facilitates microenvironment support in the bone and mammary gland.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Kochupurakkal BS, Harari D, Di-Segni A, Maik-Rachline G, Lyass L, et al. Epigen, the last ligand of ErbB receptors, reveals intricate relationships between affinity and mitogenicity. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:8503–8512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

