Transforming growth factor-β1 suppresses hepatitis B virus replication by the reduction of hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α expression
- PMID: 22276183
- PMCID: PMC3262823
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030360
Transforming growth factor-β1 suppresses hepatitis B virus replication by the reduction of hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α expression
Abstract
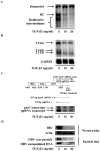
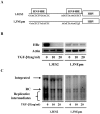
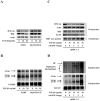
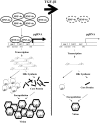
Several studies have demonstrated that cytokine-mediated noncytopathic suppression of hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication may provide an alternative therapeutic strategy for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection. In our previous study, we showed that transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-β1) could effectively suppress HBV replication at physiological concentrations. Here, we provide more evidence that TGF-β1 specifically diminishes HBV core promoter activity, which subsequently results in a reduction in the level of viral pregenomic RNA (pgRNA), core protein (HBc), nucleocapsid, and consequently suppresses HBV replication. The hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha (HNF-4α) binding element(s) within the HBV core promoter region was characterized to be responsive for the inhibitory effect of TGF-β1 on HBV regulation. Furthermore, we found that TGF-β1 treatment significantly repressed HNF-4α expression at both mRNA and protein levels. We demonstrated that RNAi-mediated depletion of HNF-4α was sufficient to reduce HBc synthesis as TGF-β1 did. Prevention of HNF-4α degradation by treating with proteasome inhibitor MG132 also prevented the inhibitory effect of TGF-β1. Finally, we confirmed that HBV replication could be rescued by ectopic expression of HNF-4α in TGF-β1-treated cells. Our data clarify the mechanism by which TGF-β1 suppresses HBV replication, primarily through modulating the expression of HNF-4α gene.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transforming growth factor-beta1 suppresses hepatitis B virus replication primarily through transcriptional inhibition of pregenomic RNA.Hepatology. 2007 Sep;46(3):672-81. doi: 10.1002/hep.21726. Hepatology. 2007. PMID: 17580335
-
Luteolin Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Replication through Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase-Mediated Down-Regulation of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4α Expression.Mol Pharm. 2016 Feb 1;13(2):568-77. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00789. Epub 2015 Dec 28. Mol Pharm. 2016. PMID: 26656210
-
[Effect of transforming growth factor-β1 on HBV replication and antigen synthesis in HepG2.2.15 cells with steatosis].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2017 Oct 20;25(10):732-737. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2017.10.003. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29108200 Chinese.
-
Nitric oxide and TGF-beta1 inhibit HNF-4alpha function in HEPG2 cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Aug 27;321(3):688-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.07.025. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15358161
-
Estrogen receptor α represses transcription of HBV genes via interaction with hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α.Gastroenterology. 2012 Apr;142(4):989-998.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.045. Epub 2012 Jan 10. Gastroenterology. 2012. PMID: 22240483
Cited by
-
Chronic hepatitis B virus and liver fibrosis: A mathematical model.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 10;13(4):e0195037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195037. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29634771 Free PMC article.
-
Doubly Spliced RNA of Hepatitis B Virus Suppresses Viral Transcription via TATA-Binding Protein and Induces Stress Granule Assembly.J Virol. 2015 Nov;89(22):11406-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00949-15. Epub 2015 Sep 2. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26339052 Free PMC article.
-
A new factor influencing pathogen detection by molecular assay in children with both mild and severe hand, foot, and mouth disease.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013 Jun;76(2):162-7. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2013.02.011. Epub 2013 Mar 25. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23535205 Free PMC article.
-
Doxorubicin Activates Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Elevation of p21 (Waf1/Cip1) and C/EBPα Expression.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 29;10(6):e0131743. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131743. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26121644 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of hepatocyte nuclear factors in hepatitis B virus infection.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Aug 21;22(31):7017-29. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.7017. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27610013 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA. 2006;295:65–73. - PubMed
-
- Farazi PA, DePinho RA. Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:674–687. - PubMed
-
- Moolla N, Kew M, Arbuthnot P. Regulatory elements of hepatitis B virus transcription. J Viral Hepat. 2002;9:323–331. - PubMed
-
- Tang H, Banks KE, Anderson AL, McLachlan A. Hepatitis B virus transcription and replication. Drug News Perspect. 2001;14:325–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

