Physical links between the nuclear envelope protein Mps3, three alternate replication factor C complexes, and a variant histone in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 22276573
- PMCID: PMC3378962
- DOI: 10.1089/dna.2011.1493
Physical links between the nuclear envelope protein Mps3, three alternate replication factor C complexes, and a variant histone in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
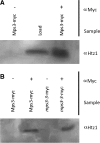
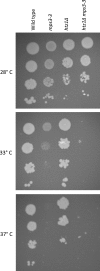
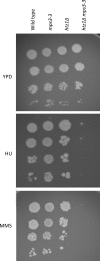
Viability of cell progeny upon cell division require that genomes are replicated, repaired, and maintained with high fidelity. Central to both DNA replication and repair are Replication Factor C (RFC) complexes which catalyze the unloading/loading of sliding clamps such as PCNA or 9-1-1 complexes on DNA. Budding yeast contain four alternate RFC complexes which play partially redundant roles. Rfc1, Ctf18, Rad24, and Elg1 are all large subunits that bind, in a mutually exclusive fashion to RFC 2-5 small subunits. Ctf18, Rad24, and Elg1 are of particular interest because, in addition to their roles in maintaining genome integrity, all three play critical roles in sister chromatid tethering reactions that appear coupled to their roles in DNA replication/repair. Intriguingly, the nuclear envelope protein Mps3 similarly exhibits roles in repair and cohesion, leading us to hypothesize that Mps3 and RFCs function through a singular mechanism. Here we report that the nuclear envelope protein Mps3 physically associates with all three of these large RFC complex subunits (Ctf18, Elg1, and Rad24). In addition we report a physical interaction between Mps3 and the histone variant Htz1, a factor previously shown to promote DNA repair. In combination, these findings reveal a direct link between the nuclear envelope and chromatin and provide support for a model that telomeres and chromatin interact with the nuclear envelope during both DNA repair and sister chromatid pairing reactions.
Figures



References
-
- Akhtar A. Gasser S.M. The nuclear envelope and transcriptional control. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:507–517. - PubMed
-
- Antoniacci L.M. Kenna M.A. Skibbens R.V. The nuclear envelope and spindle pole body-associated Mps3 protein bind telomere regulators and function in telomere clustering. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:75–79. - PubMed
-
- Antoniacci L.M. Kenna M.A. Uetz P. Fields S. Skibbens R.V. The spindle pole body assembly component mp3p/nep98p functions in sister chromatid cohesion. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:49542–49550. - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay S. Mehta M. Kuo D. Sung M.K. Chuang R. Jaehnig E.J. Bodenmiller B. Licon K. Copeland W. Shales M. Fiedler D. Dutkowski J. Guénolé A. van Attikum H. Shokat K.M. Kolodner R.D. Huh W.K. Aebersold R. Keogh M.C. Krogan N.J. Ideker T. Rewiring of genetic networks in response to DNA damage. Science. 2010;330:1385–1389. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

