Meta-analysis of p-wave dispersion values in healthy individuals: the influence of clinical characteristics
- PMID: 22276626
- PMCID: PMC6932421
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2011.00478.x
Meta-analysis of p-wave dispersion values in healthy individuals: the influence of clinical characteristics
Abstract
Background: P-wave dispersion (Pd) is an appealing marker for predicting the risk of developing atrial fibrillation. At present, no definitive cutoff value has been determined as to the diagnosis of high-risk patients. Our aims were to evaluate P-wave parameters of healthy subjects published in the literature, determine normal range and weighted means of Pd and P-wave parameters, and investigate the influences of gender, age, and BMI on the weighted results.
Methods: A systematic search of studies published in PubMed was conducted. Only studies which included control groups of healthy individuals were included.
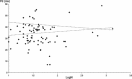
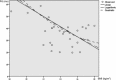
Results: Of the 657 studies initially identified, 80 were eligible for inclusion. The total number of participants was 6,827. The highest reported Pd values were 58.56 ± 16.24 ms; the lowest were 7 ± 2.7 ms. The weighted mean was 33.46 ± 9.65 ms; weighted median was 32.2 ms. Gender and age were not found to be associated with significant influences on P-wave parameter values. High-normal BMI was not found to be associated with increased P-wave parameter values.
Conclusions: Pd, Pmax, and Pmin span a wide range of values in healthy individuals. Seemingly, abnormal values were often reported in healthy adults. The high variability of P-wave parameters in healthy individuals, and overlapping of the results with those reported for patients with increased risk for atrial fibrillation, might suggest that this technique has limited sensitivity and specificity. The variability between studies may stem from methodological issues and, therefore, there is a definite need for methodological standardization of Pd measurements.
© 2012, Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Schneider MP, Hua TA, Bohm M, et al Prevention of atrial fibrillation by Renin‐Angiotensin system inhibition a meta‐analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;55:2299–2307. - PubMed
-
- Rosiak M, Dziuba M, Chudzik M, et al Risk factors for atrial fibrillation: Not always severe heart disease, not always so ‘lonely.’ Cardiol J 2010;17:437–442. - PubMed
-
- Nussinovitch N, Livneh A, Katz K, et al P wave dispersion in familial Mediterranean fever. Rheumatol Int 2011;31:1591–1594. - PubMed
-
- Michelucci A, Bagliani G, Colella A, et al P wave assessment: State of the art update. Card Electrophysiol Rev 2002;6:215–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

