Bevacizumab added to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer
- PMID: 22276821
- PMCID: PMC3401076
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1111097
Bevacizumab added to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Bevacizumab and the antimetabolites capecitabine and gemcitabine have been shown to improve outcomes when added to taxanes in patients with metastatic breast cancer. The primary aims of this trial were to determine whether the addition of capecitabine or gemcitabine to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with docetaxel, followed by doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide, would increase the rates of pathological complete response in the breast in women with operable, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative breast cancer and whether adding bevacizumab to these chemotherapy regimens would increase the rates of pathological complete response.
Methods: We randomly assigned 1206 patients to receive neoadjuvant therapy consisting of docetaxel (100 mg per square meter of body-surface area on day 1), docetaxel (75 mg per square meter on day 1) plus capecitabine (825 mg per square meter twice a day on days 1 to 14), or docetaxel (75 mg per square meter on day 1) plus gemcitabine (1000 mg per square meter on days 1 and 8) for four cycles, with all regimens followed by treatment with doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide for four cycles. Patients were also randomly assigned to receive or not to receive bevacizumab (15 mg per kilogram of body weight) for the first six cycles of chemotherapy.
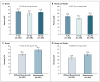
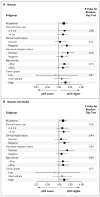
Results: The addition of capecitabine or gemcitabine to docetaxel therapy, as compared with docetaxel therapy alone, did not significantly increase the rate of pathological complete response (29.7% and 31.8%, respectively, vs. 32.7%; P=0.69). Both capecitabine and gemcitabine were associated with increased toxic effects--specifically, the hand-foot syndrome, mucositis, and neutropenia. The addition of bevacizumab significantly increased the rate of pathological complete response (28.2% without bevacizumab vs. 34.5% with bevacizumab, P=0.02). The effect of bevacizumab on the rate of pathological complete response was not the same in the hormone-receptor-positive and hormone-receptor-negative subgroups. The addition of bevacizumab increased the rates of hypertension, left ventricular systolic dysfunction, the hand-foot syndrome, and mucositis.
Conclusions: The addition of bevacizumab to neoadjuvant chemotherapy significantly increased the rate of pathological complete response, which was the primary end point of this study. (Funded by the National Cancer Institute and others; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00408408.).
Figures
Comment in
-
Fighting fire with fire: rekindling the bevacizumab debate.N Engl J Med. 2012 Jan 26;366(4):374-5. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1113368. N Engl J Med. 2012. PMID: 22276827 No abstract available.
-
Bevacizumab in neoadjuvant treatment for breast cancer.N Engl J Med. 2012 Apr 26;366(17):1637; author reply 1638-40. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1202229. N Engl J Med. 2012. PMID: 22533581 No abstract available.
-
Bevacizumab in neoadjuvant treatment for breast cancer.N Engl J Med. 2012 Apr 26;366(17):1637-8; author reply 1638-40. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1202229. N Engl J Med. 2012. PMID: 22533582 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fisher B, Brown A, Mamounas E, et al. Effect of preoperative chemotherapy on local-regional disease in women with operable breast cancer: findings from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-18. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:2483–93. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Bryant J, Wolmark N, et al. Effect of preoperative chemotherapy on the outcome of women with operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:2672–85. - PubMed
-
- Gianni L, Baselga J, Eiermann W, et al. Phase III trial evaluating the addition of paclitaxel to doxorubicin followed by cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil, as adjuvant or primary systemic therapy: European Cooperative Trial in Operable Breast Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:2474–81. - PubMed
-
- Mamounas EP, Brown A, Anderson S, et al. Sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: results from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocol B-27. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2694–702. Erratum, J Clin Oncol 2005;23:4808. - PubMed
-
- Bear HD, Anderson S, Brown A, et al. The effect on tumor response of adding sequential preoperative docetaxel to pre-operative doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide: preliminary results from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocol B-27. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:4165–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
