Multifunctional plasmonic shell-magnetic core nanoparticles for targeted diagnostics, isolation, and photothermal destruction of tumor cells
- PMID: 22276857
- PMCID: PMC3289758
- DOI: 10.1021/nn2045246
Multifunctional plasmonic shell-magnetic core nanoparticles for targeted diagnostics, isolation, and photothermal destruction of tumor cells
Abstract
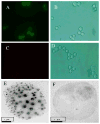
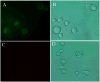
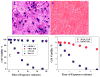
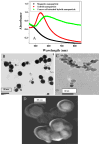
Cancer is the greatest challenge in human healthcare today. Cancer causes 7.6 million deaths and economic losses of around 1 trillion dollars every year. Early diagnosis and effective treatment of cancer are crucial for saving lives. Driven by these needs, we report the development of a multifunctional plasmonic shell-magnetic core nanotechnology-driven approach for the targeted diagnosis, isolation, and photothermal destruction of cancer cells. Experimental data show that aptamer-conjugated plasmonic/magnetic nanoparticles can be used for targeted imaging and magnetic separation of a particular kind of cell from a mixture of different cancer cells. A targeted photothermal experiment using 670 nm light at 2.5 W/cm(2) for 10 min resulted selective irreparable cellular damage to most of the cancer cells. We also showed that the aptamer-conjugated magnetic/plasmonic nanoparticle-based photothermal destruction of cancer cells is highly selective. We discuss the possible mechanism and operating principle for the targeted imaging, separation, and photothermal destruction using magnetic/plasmonic nanotechnology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Theranostic magnetic core-plasmonic shell star shape nanoparticle for the isolation of targeted rare tumor cells from whole blood, fluorescence imaging, and photothermal destruction of cancer.Mol Pharm. 2013 Mar 4;10(3):857-66. doi: 10.1021/mp300468q. Epub 2012 Nov 7. Mol Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23110457 Free PMC article.
-
Popcorn-shaped magnetic core-plasmonic shell multifunctional nanoparticles for the targeted magnetic separation and enrichment, label-free SERS imaging, and photothermal destruction of multidrug-resistant bacteria.Chemistry. 2013 Feb 18;19(8):2839-47. doi: 10.1002/chem.201202948. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Chemistry. 2013. PMID: 23296491
-
Sub-10 nm Fe3O4@Cu(2-x)S core-shell nanoparticles for dual-modal imaging and photothermal therapy.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Jun 12;135(23):8571-7. doi: 10.1021/ja4013497. Epub 2013 May 30. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 23687972
-
Magnetic-Plasmonic Core-Shell Nanoparticles: Properties, Synthesis and Applications for Cancer Detection and Treatment.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Feb 10;15(4):264. doi: 10.3390/nano15040264. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39997827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles for cancer therapy using magnetic forces.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2012 Mar;7(3):447-57. doi: 10.2217/nnm.12.10. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22385201 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Development of Nanomaterials-Based Cytosensors for the Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Aug 18;11(8):281. doi: 10.3390/bios11080281. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34436082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SNHG16 upregulation-induced positive feedback loop with YAP1/TEAD1 complex in Colorectal Cancer cell lines facilitates liver metastasis of colorectal cancer by modulating CTCs epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Aug 16;18(14):5291-5308. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.73438. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36147462 Free PMC article.
-
Theranostic magnetic core-plasmonic shell star shape nanoparticle for the isolation of targeted rare tumor cells from whole blood, fluorescence imaging, and photothermal destruction of cancer.Mol Pharm. 2013 Mar 4;10(3):857-66. doi: 10.1021/mp300468q. Epub 2012 Nov 7. Mol Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23110457 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient synthesis of a maghemite/gold hybrid nanoparticle system as a magnetic carrier for the transport of platinum-based metallotherapeutics.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jan 16;16(1):2034-51. doi: 10.3390/ijms16012034. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25603182 Free PMC article.
-
Three-dimensional (3D) plasmonic hot spots for label-free sensing and effective photothermal killing of multiple drug resistant superbugs.Nanoscale. 2016 Nov 3;8(43):18301-18308. doi: 10.1039/c6nr05888d. Nanoscale. 2016. PMID: 27714099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Møller B. Predicting the Future Burden of Cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:63–74. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. [accessed July 9, 2011]; http://www.who.int/cancer/en.
-
- National Cancer Institute. [accessed July 9, 2011]; http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/types/breast.
-
- National Cancer Institute. [accessed July 9, 2011]; http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/types/prostate.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. [accessed July 9, 2011]; http://www.cdc.gov/cancer/nbccedp.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

