Regiospecific syntheses of functionalized diaryliodonium tosylates via [hydroxy(tosyloxy)iodo]arenes generated in situ from (diacetoxyiodo)arenes
- PMID: 22276914
- PMCID: PMC3288786
- DOI: 10.1021/jo202517v
Regiospecific syntheses of functionalized diaryliodonium tosylates via [hydroxy(tosyloxy)iodo]arenes generated in situ from (diacetoxyiodo)arenes
Abstract
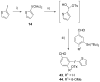
Ready access to (18)F-labeled aryl synthons is required for preparing novel radiotracers for molecular imaging with positron emission tomography. Diaryliodonium salts react with cyclotron-produced no-carrier-added [(18)F]fluoride ion to produce [(18)F]aryl fluorides. We aimed to prepare functionalized diaryliodonium salts to serve as potential precursors for producing useful (18)F-labeled aryl synthons, such as (18)F-labeled halomethylbenzenes, benzaldehydes, and benzoic acid esters. Such salts were designed to have one functionalized aryl ring, one relatively electron-rich ring, such as 4-methoxyphenyl or 2-thienyl, and a nonfluorine containing weakly nucleophilic anion. Generation of a [hydroxy(tosyloxy)iodo]arene from a functionalized (diacetoxyiodo)arene in situ followed by treatment with an electron-rich arene, such as anisole or thiophene, or with a functionalized arylstannane gave expedient regiospecific access to a wide range of functionally diverse diaryliodonium tosylates in moderate to high yields (44-98%). The described methodology broadens the scope for producing new functionalized diaryliodonium salts for diverse applications.
Figures


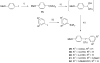
Similar articles
-
Hypervalent aryliodine compounds as precursors for radiofluorination.J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2018 Mar;61(3):196-227. doi: 10.1002/jlcr.3570. Epub 2018 Feb 5. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2018. PMID: 28981159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-step syntheses of no-carrier-added functionalized [18F]fluoroarenes as labeling synthons from diaryliodonium salts.Org Biomol Chem. 2013 Oct 7;11(37):6300-6. doi: 10.1039/c3ob41353e. Org Biomol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23942997 Free PMC article.
-
An Investigation of (Diacetoxyiodo)arenes as Precursors for Preparing No-Carrier-Added [(18)F]Fluoroarenes from Cyclotron-Produced [(18)F]Fluoride Ion.J Org Chem. 2016 Jan 4;81(1):297-302. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.5b02332. Epub 2015 Dec 17. J Org Chem. 2016. PMID: 26641128 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and Efficient Radiosyntheses of Meta-substituted [F]Fluoroarenes from [F]Fluoride Ion and Diaryliodonium Tosylates within a Microreactor.European J Org Chem. 2011 Aug;2011(23):4439-4447. doi: 10.1002/ejoc.201100382. European J Org Chem. 2011. PMID: 22016665 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorine-18 labeling of small molecules: the use of 18F-labeled aryl fluorides derived from no-carrier-added [18F]fluoride as labeling precursors.Ernst Schering Res Found Workshop. 2007;(62):51-78. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-49527-7_3. Ernst Schering Res Found Workshop. 2007. PMID: 17172152 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in α-Arylation of Carbonyl Compounds: Diaryliodonium Salts as Arylating Agents.Molecules. 2025 Jul 18;30(14):3019. doi: 10.3390/molecules30143019. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40733286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypervalent aryliodine compounds as precursors for radiofluorination.J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2018 Mar;61(3):196-227. doi: 10.1002/jlcr.3570. Epub 2018 Feb 5. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2018. PMID: 28981159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cu-Mediated C-H 18F-Fluorination of Electron-Rich (Hetero)arenes.Org Lett. 2017 Jul 21;19(14):3939-3942. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b01902. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Org Lett. 2017. PMID: 28665619 Free PMC article.
-
Single-step syntheses of no-carrier-added functionalized [18F]fluoroarenes as labeling synthons from diaryliodonium salts.Org Biomol Chem. 2013 Oct 7;11(37):6300-6. doi: 10.1039/c3ob41353e. Org Biomol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23942997 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and evaluation in monkey of [(18)F]4-fluoro-N-methyl-N-(4-(6-(methylamino)pyrimidin-4-yl)thiazol-2-yl)benzamide ([(18)F]FIMX): a promising radioligand for PET imaging of brain metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGluR1).J Med Chem. 2013 Nov 27;56(22):9146-55. doi: 10.1021/jm4012017. Epub 2013 Nov 7. J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24147864 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

