Specifically targeting ERK1 or ERK2 kills melanoma cells
- PMID: 22277029
- PMCID: PMC3305427
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-15
Specifically targeting ERK1 or ERK2 kills melanoma cells
Abstract
Background: Overcoming the notorious apoptotic resistance of melanoma cells remains a therapeutic challenge given dismal survival of patients with metastatic melanoma. However, recent clinical trials using a BRAF inhibitor revealed encouraging results for patients with advanced BRAF mutant bearing melanoma, but drug resistance accompanied by recovery of phospho-ERK (pERK) activity present challenges for this approach. While ERK1 and ERK2 are similar in amino acid composition and are frequently not distinguished in clinical reports, the possibility they regulate distinct biological functions in melanoma is largely unexplored.
Methods: Rather than indirectly inhibiting pERK by targeting upstream kinases such as BRAF or MEK, we directly (and near completely) reduced ERK1 and ERK2 using short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) to achieve sustained inhibition of pERK1 and/or pERK2.
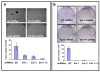
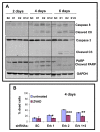
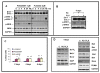
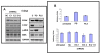
Results and discussion: Using A375 melanoma cells containing activating BRAFV600E mutation, silencing ERK1 or ERK2 revealed some differences in their biological roles, but also shared roles by reduced cell proliferation, colony formation in soft agar and induced apoptosis. By contrast, chemical mediated inhibition of mutant BRAF (PLX4032) or MEK (PD0325901) triggered less killing of melanoma cells, although they did inhibit proliferation. Death of melanoma cells by silencing ERK1 and/or ERK2 was caspase dependent and accompanied by increased levels of Bak, Bad and Bim, with reduction in p-Bad and detection of activated Bax levels and loss of mitochondrial membrane permeability. Rare treatment resistant clones accompanied silencing of either ERK1 and/or ERK2. Unexpectedly, directly targeting ERK levels also led to reduction in upstream levels of BRAF, CRAF and pMEK, thereby reinforcing the importance of silencing ERK as regards killing and bypassing drug resistance.
Conclusions: Selectively knocking down ERK1 and/or ERK2 killed A375 melanoma cells and also increased the ability of PLX4032 to kill A375 cells. Thus, a new therapeutic window is open for future clinical trials in which agents targeting ERK1 and ERK2 should be considered in patients with melanoma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The RAF inhibitor PLX4032 inhibits ERK signaling and tumor cell proliferation in a V600E BRAF-selective manner.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Aug 17;107(33):14903-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008990107. Epub 2010 Jul 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20668238 Free PMC article.
-
Reversing melanoma cross-resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors by co-targeting the AKT/mTOR pathway.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28973. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028973. Epub 2011 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22194965 Free PMC article.
-
RAF-Mutant Melanomas Differentially Depend on ERK2 Over ERK1 to Support Aberrant MAPK Pathway Activation and Cell Proliferation.Mol Cancer Res. 2021 Jun;19(6):1063-1075. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-1022. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Mol Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33707308
-
That which does not kill me makes me stronger; combining ERK1/2 pathway inhibitors and BH3 mimetics to kill tumour cells and prevent acquired resistance.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;169(8):1708-22. doi: 10.1111/bph.12220. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23647573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting melanoma by small molecules: challenges ahead.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013 Jul;26(4):464-9. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12109. Epub 2013 May 28. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013. PMID: 23611259 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activated ERK Signaling Is One of the Major Hub Signals Related to the Acquisition of Radiotherapy-Resistant MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 6;22(9):4940. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094940. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34066541 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) hyperactivation and enhanced NRAS expression drive acquired vemurafenib resistance in V600E BRAF melanoma cells.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 3;289(40):27714-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.532432. Epub 2014 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25063807 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Proliferative, Pro-Apoptotic, Anti-Migrative and Tumor-Inhibitory Effects and Pleiotropic Mechanism of Theaflavin on B16F10 Melanoma Cells.Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Feb 25;14:1291-1304. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S286350. eCollection 2021. Onco Targets Ther. 2021. PMID: 33658796 Free PMC article.
-
Early decline in serum phospho-CSE1L levels in vemurafenib/sunitinib-treated melanoma and sorafenib/lapatinib-treated colorectal tumor xenografts.J Transl Med. 2015 Jun 13;13:191. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0553-6. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26070816 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated pathways to both apoptosis and autophagy: Significance for melanoma treatment.World J Exp Med. 2015 Nov 20;5(4):206-17. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v5.i4.206. eCollection 2015 Nov 20. World J Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26618107 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

