The role of nutraceutical supplements in the treatment of dyslipidemia
- PMID: 22277145
- PMCID: PMC9645405
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2011.00576.x
The role of nutraceutical supplements in the treatment of dyslipidemia
Abstract
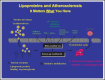
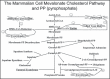
The combination of a lipid-lowering diet and scientifically proven nutraceutical supplements has the ability to significantly reduce low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, increase LDL particle size, decrease LDL particle number, lower trigylcerides and very LDL levels, and increase total and high-density lipoprotein 2b cholesterol. In addition, inflammation, oxidative stress, and immune responses are decreased. In several prospective clinical trials, coronary heart disease and cardiovascular disease have been reduced with many nutraceutical supplements. This nutritional and nutraceutical supplement treatment is a valid alternative for patients who are intolerant to statins, cannot take other drugs for the treatment of dyslipidemia, or prefer alternative treatments. This new approach to lipid management to decrease vascular disease utilizes a functional medicine approach with a broader treatment program that will address the multitude of steps involved in lipid-induced vascular damage.
© 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Kannel WB, Castelli WD, Gordon T, et al. Serum cholesterol, lipoproteins and risk of coronary artery disease. The Framingham Study. Ann Intern Med. 1971;74:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Houston MC. Nutrition and nutraceutical supplements in the treatment of hypertension. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2010;8:821–833. - PubMed
-
- Houston MC, Fazio S, Chilton FH, et al. Non pharmacologic treatment of dyslipidemia. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2009;52:61–94. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

