Pleurotomy with subxyphoid pleural drain affords similar effects to pleural integrity in pulmonary function after off-pump coronary artery bypass graft
- PMID: 22277597
- PMCID: PMC3292451
- DOI: 10.1186/1749-8090-7-11
Pleurotomy with subxyphoid pleural drain affords similar effects to pleural integrity in pulmonary function after off-pump coronary artery bypass graft
Abstract
Background: Exacerbation of pulmonary dysfunction has been reported in patients receiving a pleural drain inserted through the intercostal space in comparison to patients with an intact pleura undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). Evidence suggests that shifting the site of pleural drain insertion to the subxyphoid position minimizes chest wall trauma and preserves respiratory function in the early postoperative period. The aim of this study was to compare the pulmonary function parameters, clinical outcomes, and pain score between patients undergoing pleurotomy with pleural drain placed in the subxyphoid position and patients with intact pleural cavity after off-pump CABG (OPCAB) using left internal thoracic artery (LITA).
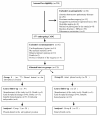
Methods: Seventy-one patients were allocated into two groups: I (n = 38 open left pleural cavity and pleural drain inserted in the subxyphoid position); II (n = 33 intact pleural cavity). Pulmonary function tests and clinical parameters were recorded preoperatively and on postoperative days (POD) 1, 3 and 5. Arterial blood gas analysis and shunt fraction were evaluated preoperatively and in POD1. Pain score was assessed on POD1. To monitor pleural effusion and atelectasis chest radiography was performed routinely 1 day before operation and until POD5.
Results: In both groups a significant impairment was found in lung function parameters until on POD5. However, no significant difference in forced vital capacity and forced expiratory volume in 1 second were seen between groups. A significant decrease in partial pressure of arterial oxygen and an increase in shunt fraction values were observed on POD1 in both groups, but no statistical difference was found when the groups were compared. Pleural effusion and atelectasis until on POD5 were similar in both groups. There were no statistical differences in pain score, duration of mechanical ventilation and postoperative hospital stay between groups.
Conclusion: Subxyphoid insertion of pleural drain provides similar effects to preserved pleural integrity in pulmonary function, clinical outcomes, and thoracic pain after OPCAB. Therefore, our results support the hypothesis that once pleural cavities are incidentally or purposely opened during LITA dissection, subxyphoid placement of the pleural drain is recommended.
Similar articles
-
Pleural subxyphoid drain confers better pulmonary function and clinical outcomes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease after off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting: a randomized controlled trial.Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 2014 Oct-Dec;29(4):588-94. doi: 10.5935/1678-9741.20140047. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 2014. PMID: 25714214 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Subxyphoid pleural drain confers lesser impairment in respiratory muscle strength, oxygenation and lower chest pain after off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting: a randomized controlled trial.Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 2012 Jan-Mar;27(1):103-9. doi: 10.5935/1678-9741.20120015. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 2012. PMID: 22729307 Clinical Trial.
-
Sub-xyphoid pleural drain as a determinant of functional capacity and clinical results after off-pump coronary artery bypass surgery: a randomized clinical trial.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2014 Sep;19(3):382-7. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivu138. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2014. PMID: 24899589 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of Intercostal and Subxiphoid Left Pleural Drain After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Jun 5;16(6):e61710. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61710. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38975421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does a skeletonized internal thoracic artery give fewer postoperative complications than a pedicled artery for patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting?Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015 May;20(5):663-8. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivv026. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015. PMID: 25712987 Review.
Cited by
-
Pleural subxyphoid drain confers better pulmonary function and clinical outcomes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease after off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting: a randomized controlled trial.Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 2014 Oct-Dec;29(4):588-94. doi: 10.5935/1678-9741.20140047. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 2014. PMID: 25714214 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Subxiphoid single-port video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery.J Vis Surg. 2016 Jul 1;2:112. doi: 10.21037/jovs.2016.06.08. eCollection 2016. J Vis Surg. 2016. PMID: 29399498 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of continuous positive airway pressure associated to exercise on the breathing pattern and heart rate variability of patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting surgery: a randomized controlled trial.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021 Aug 20;54(11):e10974. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2021e10974. eCollection 2021. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021. PMID: 34431871 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Early Open-Lung Ventilation Improves Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Left Cardiac Dysfunction Undergoing Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass: a Randomized Controlled Trial.Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2016 Sep-Oct;31(5):358-364. doi: 10.5935/1678-9741.20160057. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2016. PMID: 27982344 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Analgesic efficacy of lidocaine and multimodal analgesia for chest tube removal: A randomized trial study.Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2015 Nov-Dec;23(6):1000-6. doi: 10.1590/0104-1169.0498.2642. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2015. PMID: 26625989 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Burgess GE, Cooper JR, Marino RJ, Peuler MJ, Mills NL, Ochsner JL. Pulmonary effect of pleurotomy during and after coronary artery bypass with internal mammary artery versus saphenous vein grafts. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1978;76:230–4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources