Mechanisms of acquired crizotinib resistance in ALK-rearranged lung Cancers
- PMID: 22277784
- PMCID: PMC3385512
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003316
Mechanisms of acquired crizotinib resistance in ALK-rearranged lung Cancers
Abstract
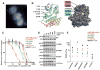
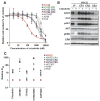
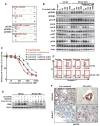
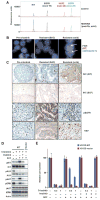
Most anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) are highly responsive to treatment with ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). However, patients with these cancers invariably relapse, typically within 1 year, because of the development of drug resistance. Herein, we report findings from a series of lung cancer patients (n = 18) with acquired resistance to the ALK TKI crizotinib. In about one-fourth of patients, we identified a diverse array of secondary mutations distributed throughout the ALK TK domain, including new resistance mutations located in the solvent-exposed region of the adenosine triphosphate-binding pocket, as well as amplification of the ALK fusion gene. Next-generation ALK inhibitors, developed to overcome crizotinib resistance, had differing potencies against specific resistance mutations. In addition to secondary ALK mutations and ALK gene amplification, we also identified aberrant activation of other kinases including marked amplification of KIT and increased autophosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor in drug-resistant tumors from patients. In a subset of patients, we found evidence of multiple resistance mechanisms developing simultaneously. These results highlight the unique features of TKI resistance in ALK-positive NSCLCs and provide the rationale for pursuing combinatorial therapeutics that are tailored to the precise resistance mechanisms identified in patients who relapse on crizotinib treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Escaping ALK inhibition: mechanisms of and strategies to overcome resistance.Sci Transl Med. 2012 Feb 8;4(120):120ps2. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003728. Sci Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22323827
References
-
- Chiarle R, Voena C, Ambrogio C, Piva R, Inghirami G. The anaplastic lymphoma kinase in the pathogenesis of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:11–23. - PubMed
-
- Janoueix-Lerosey I, Lequin D, Brugières L, Ribeiro A, de Pontual L, Combaret V, Raynal V, Puisieux A, Schleiermacher G, Pierron G, Valteau-Couanet D, Frebourg T, Michon J, Lyonnet S, Amiel J, Delattre O. Somatic and germline activating mutations of the ALK kinase receptor in neuroblastoma. Nature. 2008;455:967–970. - PubMed
-
- George RE, Sanda T, Hanna M, Fröhling S, Luther W, II, Zhang J, Ahn Y, Zhou W, London WB, McGrady P, Xue L, Zozulya S, Gregor VE, Webb TR, Gray NS, Gilliland DG, Diller L, Greulich H, Morris SW, Meyerson M, Look AT. Activating mutations in ALK provide a therapeutic target in neuroblastoma. Nature. 2008;455:975–978. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Takita J, Choi YL, Kato M, Ohira M, Sanada M, Wang L, Soda M, Kikuchi A, Igarashi T, Nakagawara A, Hayashi Y, Mano H, Ogawa S. Oncogenic mutations of ALK kinase in neuroblastoma. Nature. 2008;455:971–974. - PubMed
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, Fujiwara S, Watanabe H, Kurashina K, Hatanaka H, Bando M, Ohno S, Ishikawa Y, Aburatani H, Niki T, Sohara Y, Sugiyama Y, Mano H. Identification of the transforming EML4–ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561–566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

