Early maternal undernutrition programs increased feed intake, altered glucose metabolism and insulin secretion, and liver function in aged female offspring
- PMID: 22277936
- PMCID: PMC3330774
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00241.2011
Early maternal undernutrition programs increased feed intake, altered glucose metabolism and insulin secretion, and liver function in aged female offspring
Abstract
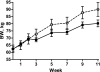
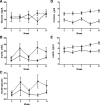
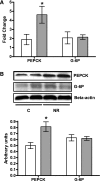
Insulin resistance and obesity are components of the metabolic syndrome that includes development of cardiovascular disease and diabetes with advancing age. The thrifty phenotype hypothesis suggests that offspring of poorly nourished mothers are predisposed to the various components of the metabolic syndrome due to adaptations made during fetal development. We assessed the effects of maternal nutrient restriction in early gestation on feeding behavior, insulin and glucose dynamics, body composition, and liver function in aged female offspring of ewes fed either a nutrient-restricted [NR 50% National Research Council (NRC) recommendations] or control (C: 100% NRC) diet from 28 to 78 days of gestation, after which both groups were fed at 100% of NRC from day 79 to lambing and through lactation. Female lambs born to NR and C dams were reared as a single group from weaning, and thereafter, they were fed 100% NRC recommendations until assigned to this study at 6 yr of age. These female offspring were evaluated by a frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance test, followed by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for body composition analysis prior to and after ad libitum feeding of a highly palatable pelleted diet for 11 wk with automated monitoring of feed intake (GrowSafe Systems). Aged female offspring born to NR ewes demonstrated greater and more rapid feed intake, greater body weight gain, and efficiency of gain, lower insulin sensitivity, higher insulin secretion, and greater hepatic lipid and glycogen content than offspring from C ewes. These data confirm an increased metabolic "thriftiness" of offspring born to NR mothers, which continues into advanced age, possibly predisposing these offspring to metabolic disease.
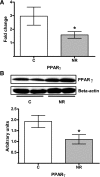
Figures
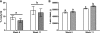
References
-
- Ahren B, Pacini G. Importance of quantifying insulin secretion in relation to insulin sensitivity to accurately assess beta cell function in clinical studies. Eur J Endocrinol 150: 97–104, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med 346: 1221–1231, 2002 - PubMed
-
- AOAC International Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of the Official Analytical Chemists. 15th ed Arlington, VA: AOAC International, 1990
-
- Azzout-Marniche D, Guadichon C, Blouet C, Bos C, Mathe V, Huneau JF, Tome D. Liver glyconeogenesis: a pathway to cope with postprandial amino acid excess in high-protein fed rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 292: R1400–R1407, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Beard JC, Bergman RN, Ward WK, Porte D., Jr The insulin sensitivity index in nondiabetic man. Correlation between clamp-derived and IVGTT-derived values. Diabetes 35: 362–369, 1986 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

